caddy 配置摸索
2023-05-31
caddy command 常用命令
caddy 原地更新配置
caddy reload --config /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
caddy reload --config /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
2023/06/03 08:33:47.291 INFO using provided configuration {"config_file": "/etc/caddy/Caddyfile", "config_adapter": ""}
/srv # ps aux | grep caddy
1 root 0:00 caddy run --config /etc/caddy/Caddyfile --adapter caddyfile
caddy 配置格式化
# 查看格式化的文档变化预览
caddy fmt /etc/caddy/Caddyfile --diff
# 原地格式化
caddy fmt /etc/caddy/Caddyfile --overwrite
caddy fmt
Formats the Caddyfile by adding proper indentation and spaces to improve
human readability. It prints the result to stdout.
If --overwrite is specified, the output will be written to the config file
directly instead of printing it.
If --diff is specified, the output will be compared against the input, and
lines will be prefixed with '-' and '+' where they differ. Note that
unchanged lines are prefixed with two spaces for alignment, and that this
is not a valid patch format.
caddy configs
handle vs handle_path
hanle_path会自动把转发到前缀去掉, handle则不会, url会保留到后端, 需要看情况进行额外处理.
https://caddyserver.com/docs/caddyfile/directives/handle_path
Same as the handle directive, but implicitly strips the matched path prefix.
Handling a request matching a certain path (while stripping that path from the request URI) is a common enough use case that it has its own directive for convenience.
This configuration:
handle_path /prefix/* {
...
}
is effectively the same as this:
handle /prefix/* {
uri strip_prefix /prefix
...
}
but the handle_path form is slightly more succinct.
file_server
https://caddyserver.com/docs/caddyfile/directives/file_server
file_servrer会与root搭配使用, 用于指定静态文件搜索的地址范围.
Most often, the file_server directive is paired with the root directive to set the file root for the whole site, but this directive also has a root subdirective (below) to set the root only for this handler if preferred. Note that a site root does not carry sandbox guarantees: the file server does prevent directory traversal from path components, but symbolic links within the root can still allow accesses outside of the root.
file_server内部的root, 则可以专门配置给file_server使用.
root sets the path to the site root. It's similar to the root directive except it applies to this file server instance only and overrides any other site root that may have been defined. Default: {http.vars.root} or the current working directory. Note: This subdirective only changes the root for this handler. For other directives (like try_files or templates) to know the same site root, use the root directive, not this subdirective.
file_server [<matcher>] [browse] {
fs <backend...>
root <path>
hide <files...>
index <filenames...>
browse [<template_file>]
precompressed <formats...>
status <status>
disable_canonical_uris
pass_thru
}
配置header与cors
domain.com {
header {
+Access-Control-Allow-Origin: domain2.com.cn
}
}
https://caddyserver.com/docs/caddyfile/directives/header
header [<matcher>] [[+|-|?]<field> [<value>|<find>] [<replace>]] {
# Replace
<field> <find> <replace>
# Add or Set
[+]<field> <value>
# Delete
-<field>
# Default
?<field> <value>
[defer]
}
file_server
咨询了chatgpt, 使用root命令后其实就有静态文件托管的能力了, 不过要设置精细化的管控比如gzip压缩之类, 还是需要设置file_server才行.
caddy wordpress 配置 chatgpt 咨询
2023-05-31
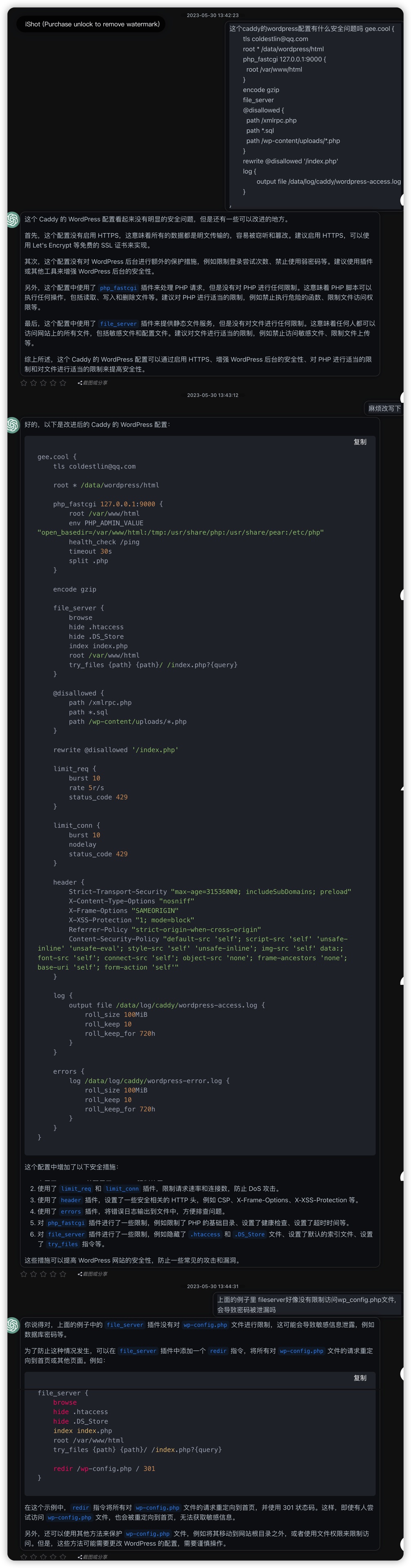
静态文件站点caddy托管还好, 没什么安全问题, 但是wordpress托管就不一样了. wordpress的php后台代码配置和页面静态文件都在同一个地方, 很容易就把密码配置泄漏出去了. 一个是担心站点被恶意脚本远程执行, 另一个是担心的是配置了file_server, 所有文件被直接获取下载了.
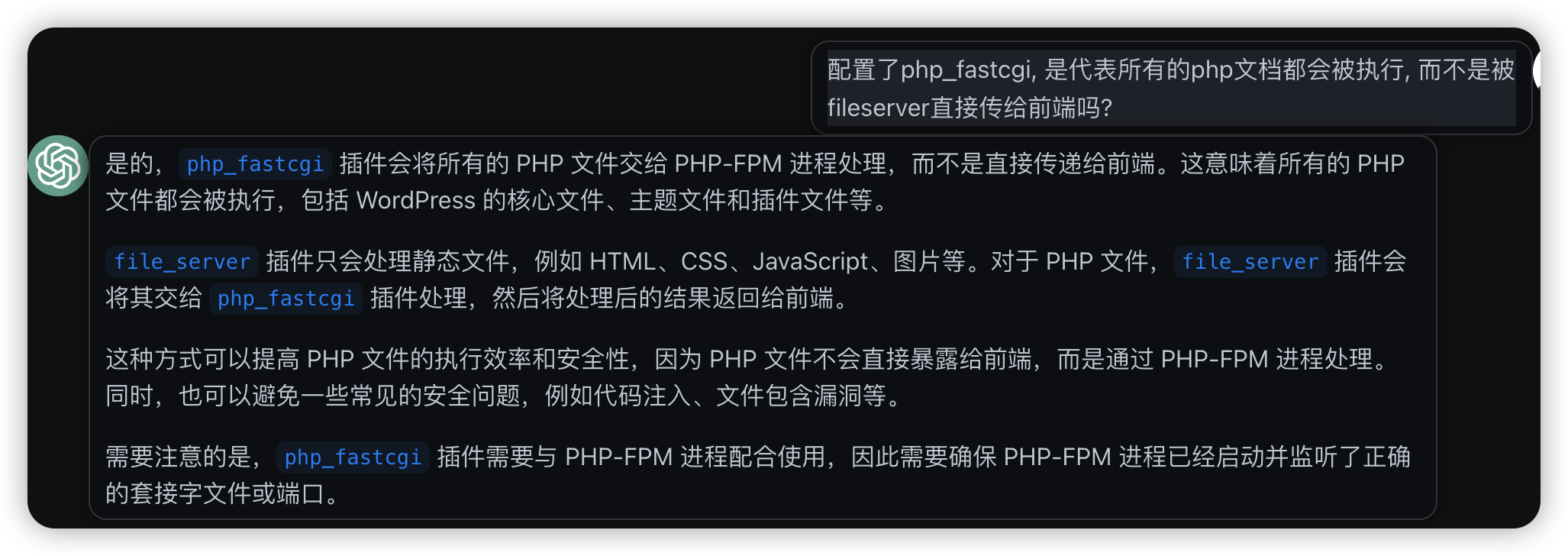
咨询了chatgpt安全问题, 有php_fpm后, php文件就不会被当做静态文件直接传给前端, 而是交给php_fpm执行后再返回. 同时chatgpt还给出了一堆其他的建议, 比如可以限流限ip, 比如担心某些php文件被执行, 可以直接设置301转发.
另外现在都不建议把账号密码写在wordpress的config.php文件里了, 直接用环境变量, 至少安全许多.
有了chatgpt, nginx/caddy这类配置的心智负担也能减少许多了, 不过一下子给出了一堆的配置修改, 还是得自己一项一项去核实才能知道会不会被chatgpt坑了, 但至少思路和修改基础方法都有了.