java执行bash命令与观察
java执行bash命令与观察, 并且设置超时时间.
咨询chatgpt, 各种场景都能提供不错的代码. 不过从对话过程也可以看出来, 如果自己没有考虑多一点, 不停给反馈, chatgpt不会直接提供更好的方法.
有了chatgpt之后, 许多技术细节的实现门槛真的低了好多, 不用到处去翻博客和源码才能找到蛛丝马迹进行参考了.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ShellTask implements Callable<String> {
private final String command;
private Process process;
public ShellTask(String command) {
this.command = command;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
output.append(line).append("\n");
}
reader.close();
process.waitFor();
return output.toString();
}
public void cancel() {
if (process != null) {
process.destroy();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String command = "your_shell_command";
long timeout = 60000; // Timeout in milliseconds (e.g., 60 seconds)
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
ShellTask shellTask = new ShellTask(command);
Future<String> future = executor.submit(shellTask);
try {
String result = future.get(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
future.cancel(true);
shellTask.cancel();
System.out.println("Shell task timed out and was terminated.");
}
executor.shutdown();
}
}
咨询过程记录:
Q: 麻烦写一段java 代码: java 开启新线程执行shell任务, 时刻获取shell的日志信息, 并且在shell超时的时候主动终止
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class ShellTask implements Runnable {
private final String command;
private final long timeout;
public ShellTask(String command, long timeout) {
this.command = command;
this.timeout = timeout;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Process process;
try {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
String line;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime > timeout) {
process.destroy();
System.out.println("Shell task timed out and was terminated.");
break;
}
}
reader.close();
process.waitFor();
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String command = "your_shell_command";
long timeout = 60000; // Timeout in milliseconds (e.g., 60 seconds)
Thread thread = new Thread(new ShellTask(command, timeout));
thread.start();
}
}
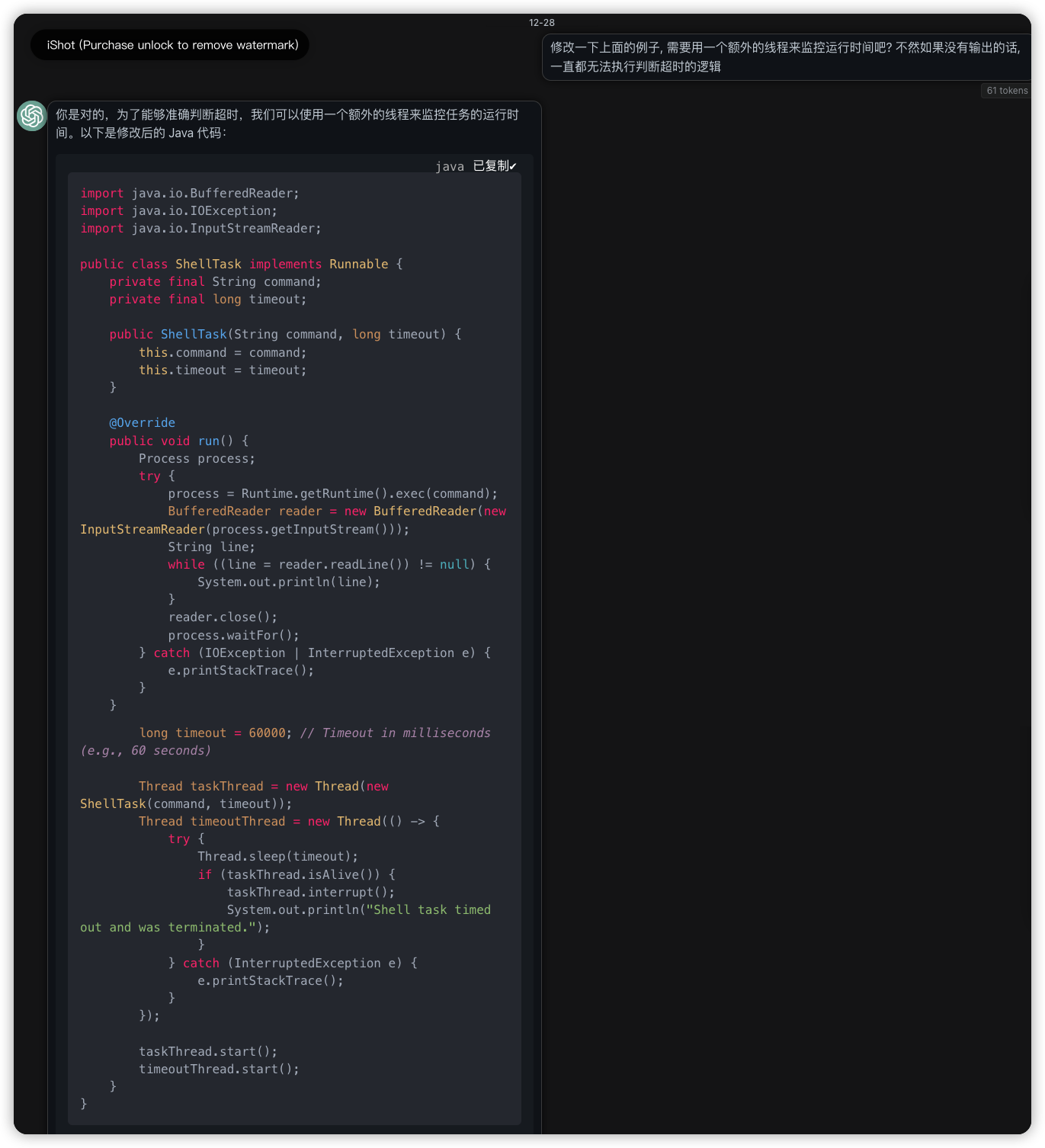
Q: 修改一下上面的例子, 需要用一个额外的线程来监控运行时间吧? 不然如果没有输出的话, 一直都无法执行判断超时的逻辑
A:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class ShellTask implements Runnable {
private final String command;
private final long timeout;
public ShellTask(String command, long timeout) {
this.command = command;
this.timeout = timeout;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Process process;
try {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
reader.close();
process.waitFor();
} catch (IOException | InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String command = "your_shell_command";
long timeout = 60000; // Timeout in milliseconds (e.g., 60 seconds)
Thread taskThread = new Thread(new ShellTask(command, timeout));
Thread timeoutThread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(timeout);
if (taskThread.isAlive()) {
taskThread.interrupt();
System.out.println("Shell task timed out and was terminated.");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
taskThread.start();
timeoutThread.start();
}
}
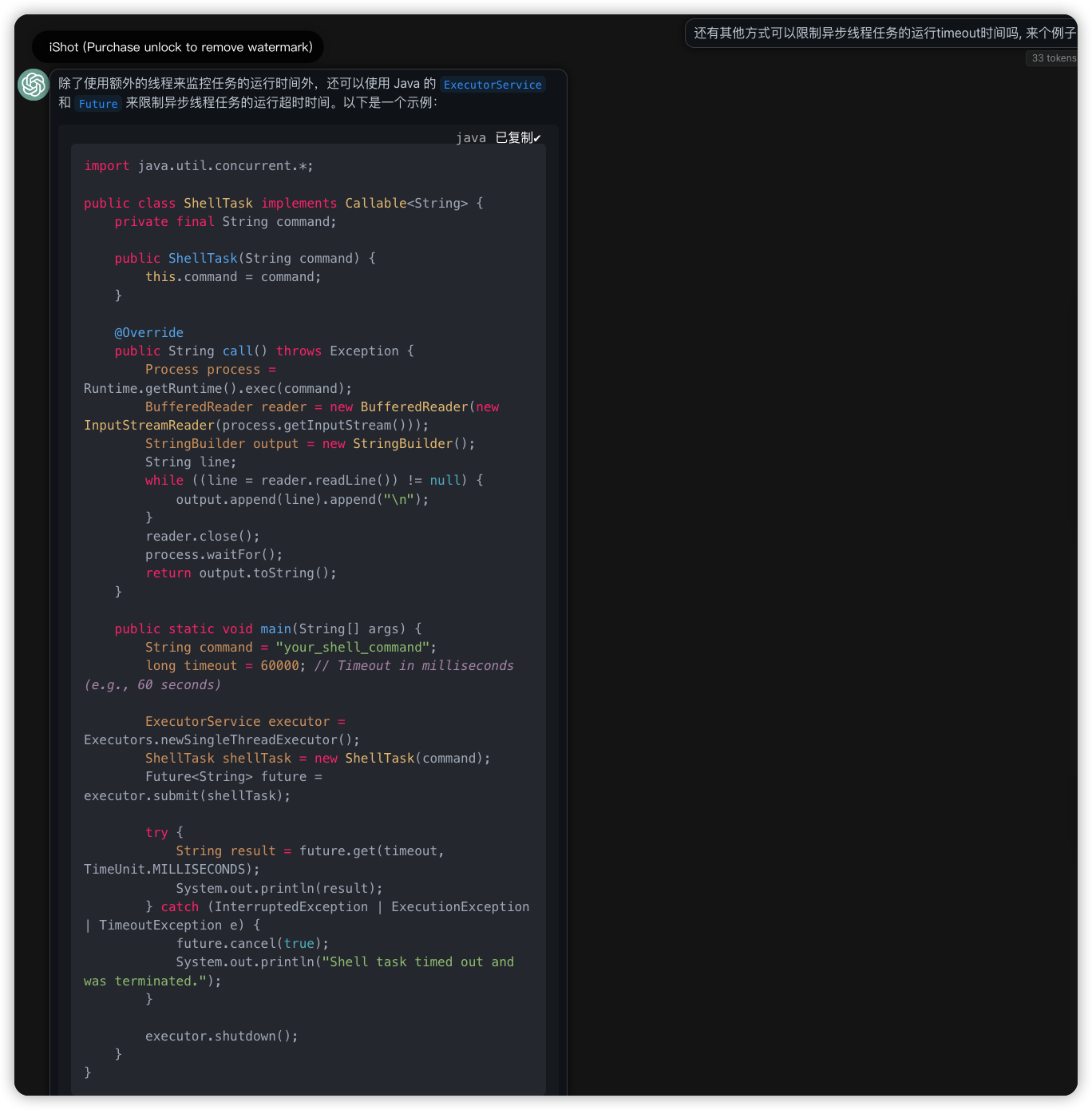
Q: 还有其他方式可以限制异步线程任务的运行timeout时间吗, 来个例子
A: 除了使用额外的线程来监控任务的运行时间外,还可以使用 Java 的 ExecutorService 和 Future 来限制异步线程任务的运行超时时间。以下是一个示例:
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ShellTask implements Callable<String> {
private final String command;
public ShellTask(String command) {
this.command = command;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
output.append(line).append("\n");
}
reader.close();
process.waitFor();
return output.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String command = "your_shell_command";
long timeout = 60000; // Timeout in milliseconds (e.g., 60 seconds)
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
ShellTask shellTask = new ShellTask(command);
Future<String> future = executor.submit(shellTask);
try {
String result = future.get(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
future.cancel(true);
System.out.println("Shell task timed out and was terminated.");
}
executor.shutdown();
}
}
Q: process.waitFor() 什么意思? Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command); 是什么, 马上在本线程执行脚本命令吗
A:
process.waitFor() 是一个阻塞方法,它会等待当前进程执行完毕并返回退出状态码。在上述代码中,process.waitFor() 用于等待 shell 命令执行完成。
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command) 是 Java 中用于执行外部命令的方法。它会创建一个新的进程来执行指定的命令。在上述代码中,Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command) 会在当前线程中启动一个新的进程来执行 command 所代表的 shell 命令。
需要注意的是,Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command) 方法会返回一个 Process 对象,通过该对象可以获取到执行命令的输入流、输出流和错误流。在示例代码中,我们使用 process.getInputStream() 获取命令的输出流,并通过 BufferedReader 逐行读取输出。
然而,Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command) 并不会立即执行命令,而是启动一个新的进程来执行命令。在执行命令期间,你可以通过 process.getInputStream() 获取命令的输出,并通过 process.waitFor() 等待命令执行完成。
需要注意的是,Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command) 方法在执行命令时可能会抛出 IOException,因此需要进行异常处理。
总结起来,Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command) 方法会在当前线程中启动一个新的进程来执行指定的 shell 命令,并返回一个 Process 对象。process.waitFor() 方法用于等待命令执行完成。
Q: 异步线程里执行Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command) 创建新的进程来执行指定的命令 , 然后通过 future.cancel(true); 的时候, 可以阻止线程里的新进程吗?
A:
在 Java 中,通过 Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command) 创建的新进程是与当前 Java 进程独立的子进程。当你调用 future.cancel(true) 取消任务时,它会尝试中断任务的执行,但无法直接控制和终止子进程。
future.cancel(true) 方法会尝试中断任务的执行,但具体是否能够成功中断取决于任务本身的实现。对于通过 Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command) 创建的子进程,中断操作不会直接影响子进程的执行。
如果你希望在取消任务时终止子进程,可以使用 Process 对象的 destroy() 方法来终止子进程的执行。在你调用 future.cancel(true) 取消任务后,你可以通过 Process 对象的引用来调用 destroy() 方法。
以下是一个示例,演示如何在取消任务时终止子进程的执行:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ShellTask implements Callable<String> {
private final String command;
private Process process;
public ShellTask(String command) {
this.command = command;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
output.append(line).append("\n");
}
reader.close();
process.waitFor();
return output.toString();
}
public void cancel() {
if (process != null) {
process.destroy();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String command = "your_shell_command";
long timeout = 60000; // Timeout in milliseconds (e.g., 60 seconds)
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
ShellTask shellTask = new ShellTask(command);
Future<String> future = executor.submit(shellTask);
try {
String result = future.get(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
future.cancel(true);
shellTask.cancel();
System.out.println("Shell task timed out and was terminated.");
}
executor.shutdown();
}
}
在上述代码中,我们修改了 ShellTask 类,添加了一个 cancel() 方法,用于终止子进程的执行。在 cancel() 方法中,我们调用 process.destroy() 来终止子进程。
在 main() 方法中,我们在取消任务时调用了 shellTask.cancel() 方法,以确保终止子进程的执行。
请注意,process.destroy() 方法会强制终止子进程,因此需要谨慎使用。在终止子进程时,可能会导致资源泄漏或不完在终止子进程时,可能会导致资源泄漏或不完全清理的情况。因此,在使用 process.destroy() 终止子进程之前,你可能需要进行一些清理操作,例如关闭输入流、输出流和错误流。
以下是一个修改后的示例代码,演示了如何在终止子进程之前进行资源清理
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ShellTask implements Callable<String> {
private final String command;
private Process process;
public ShellTask(String command) {
this.command = command;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder();
String line;
try {
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
output.append(line).append("\n");
}
} finally {
reader.close();
}
process.waitFor();
return output.toString();
}
public void cancel() {
if (process != null) {
process.destroy();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String command = "your_shell_command";
long timeout = 60000; // Timeout in milliseconds (e.g., 60 seconds)
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
ShellTask shellTask = new ShellTask(command);
Future<String> future = executor.submit(shellTask);
try {
String result = future.get(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
future.cancel(true);
shellTask.cancel();
System.out.println("Shell task timed out and was terminated.");
}
executor.shutdown();
}
}