spark context thrift server stuff
阅读kyuubi期间的一些杂七杂八的记录, kyuubi那边记录比较完整一些.
spark thrift server
spark与hive的搭配选项实在太多了, spark直接读取hive metastore, 然后自行执行; spark通过spark thrift server执行查询; hive on spark, hive的执行引擎从mr/tez切换为spark...
看spark的代码, 在sql里面可以看到有两个hive子文件夹, sql/hive和sql/hive-thriftserver.
前者就是spark标准处理hive的流程, 从hive metastore直接读取元数据信息, spark直接做sql解析, 转换成spark job进行执行, 本质上每个连接就是一个spark submit提交的application.
后者是一个独立的服务, 启动了spark thrift server(sts),用的是hive server的thrift框架, 只是sql解析和执行的部分已经做了spark的替换. 通过sts, spark可以对外提供jdbc服务, 一些sql客户端可以直接连接spark, 当做mysql之类的数据库进行使用. spark thrift application里也支持ranger的hive sql管控, 可以通过配置完成,代码里能看到一些权限管控代码. (但这时候也有问题, kyuubi一直说spark sts是单租户, 启动的时候就确定了用户和资源. 整个sts的真实用户只有一个, ranger的管控作用非常有限?)
搞数据治理集群管控才会关心这些细节, 什么连接方式sql管控能生效, 什么提交方式用户认证能生效, 真是没完没了. 对于普通spark用户而言, jdbc连接sql直接执行, 啥都不用管. 只要限制用户的使用场景, 内部的数据治理平台也不用管那么多.
cloudera文档 sparksql
Chapter 7. Using Spark SQL
spark sql的使用方式,左边是spark shell, 右边是jdbc通过thrift server访问.
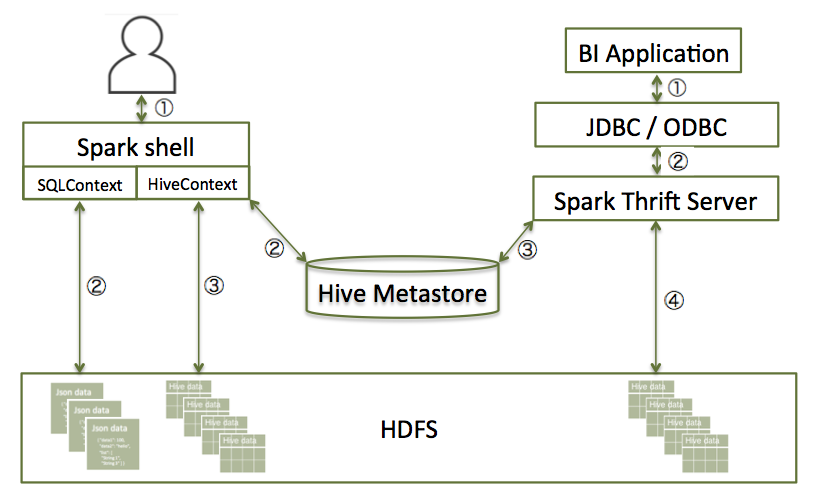
Spark SQL can read data directly from the filesystem, when SQLContext is used. This is useful when the data you are trying to analyze does not reside in Hive (for example, JSON files stored in HDFS).
Spark SQL can also read data by interacting with the Hive MetaStore, when HiveContext is used. If you already use Hive, you should use HiveContext; it supports all Hive data formats and user-defined functions (UDFs), and allows full access to the HiveQL parser. HiveContext extends SQLContext, so HiveContext supports all SQLContext functionality.
jdbc访问spark sql
clouder的官方使用文档, 还是提供了不少使用上的信息. 比如spark thrift server 工作在yarn client模式; 不支持doAs用户认证, 需要通过spark shell或者代码api进行绕过; 所有用户jdbc请求共享同一个spark context.
Accessing Spark SQL through JDBC and ODBC
- The Spark Thrift Server works in YARN client mode only.
- ODBC and JDBC client configurations must match Spark Thrift Server configuration parameters. For example, if the Thrift Server is configured to listen in binary mode, the client should send binary requests and use HTTP mode when the Thrift Server is configured over HTTP.
- When using JDBC or ODBC to access Spark SQL in a production environment, note that the Spark Thrift Server does not currently support the doAs authorization property, which propagates user identity. Workaround: use programmatic APIs or spark-shell, submitting the job under your identity.
- All client requests coming to Spark Thrift Server share a SparkContext.
beeline> !connect jdbc:hive2://localhost:10015
Connecting to jdbc:hive2://localhost:10015
Enter username for jdbc:hive2://localhost:10015:
Enter password for jdbc:hive2://localhost:10015:
...
Connected to: Spark SQL (version 1.6.1)
Driver: Spark Project Core (version 1.6.1.2.4.0.0-169)
Transaction isolation: TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10015>
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10015> show tables;
+------------+--------------+--+
| tableName | isTemporary |
+------------+--------------+--+
| sample_07 | false |
| sample_08 | false |
| testtable | false |
+------------+--------------+--+
3 rows selected (2.399 seconds)
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10015>
spark shell 访问spark sql
Accessing Spark SQL Through the Spark Shell
通过spark shell的方式访问spark sql, 一并对比下.
./bin/spark-shell --num-executors 1 --executor-memory 512m --master yarn-client
- To read data directly from the filesystem, construct a SQLContext. For an example that uses SQLContext and the Spark DataFrame API to access a JSON file, see Using the Spark DataFrame API.
- To read data by interacting with the Hive MetaStore, construct a HiveContext. (HiveContext extends SQLContext.) For an example of the use of HiveContext (instantiated as val sqlContext), see Accessing ORC Files from Spark.
一些spark context和spark thrift server的博客
spark context 是一个重客户端
每个spark-submit的spark application都是一个独立完整的应用, 在提交获取资源后可以独立于spark master这些中间节点运行, 因此各种依赖配置都会同时打包带上, 不依赖外部集群的依赖单独运行. 所以spark应用彼此之间独立性很强, 同时每个spark应用的依赖包都会比较大, 启动也会比较慢.
Spark-Applications-Are-Fat
https://www.russellspitzer.com/2017/02/03/Spark-Applications-Are-Fat/
One Line Summary: Any applications which use a Spark Context should be started with dse spark-submit in place of java -jar because they need full cluster configuration.
A common question that comes up when we talk about Spark is “Why does my Spark Application require so many libraries and configuration? Why can’t i just run java -jar foo.jar?” The main reason for this is that any application that uses a Spark Context is implicitly a Fat Client for Spark which requires all the setup and configuration of a full Spark cluster.
Every Spark Application is basically a completely isolated set of distributed JVMs. The Spark Driver is basically the scheduler/master while the executors are its workers.
This architecture means that even a statement like spark.sql(“SELECT * FROM lah”) requires the Spark Driver to do all of the following
- Negotiating the creation of the remote JVMs with the Spark Master
- Initiating two way communication with every Executor JVM created
- Management of liveness of all remote machines
- Creation of a catalogue of Sql Table and Keyspace definitions (held locally but this may involve communicating with a remote metastore)
- Parsing and optimizing the query
- Conversion of the query into a set of compiled at runtime java code
- Sending out the newly compiled java code
- Dividing the query into chunks to be processed
- Distribution of those chunks
- Tracking the completed locations of those chunks
- Redistributing metadata to let executors know what additional work they should do and where those completed chunks are
- Negotiating shuffles between executor JVMS incase chunks need to be co-grouped
- Gathering back the results from all of the remote executors
All of this work means a considerable amount of configuration and classpath organization has to happen. This simple statement basically has to know how to completely run a Spark Cluster in order to execute. All optimizations, filters, custom datatypes, classloader specifications, and cluster configuration notes need to be set correctly for just that tiny statement to run in an isolated application.
Most users come in with an expectation that Spark will operate instead in a workflow like
- Send a request
- Receive a response
We cannot do this with a single Spark Standalone application.
To achieve this kind uncoupled behavior we direct users to use a different architecture where the machinery of the Spark Application is separate from the Application using Spark Results. This environment is created by running a Spark Driver like the SparkJobserver, SparkSQLThriftServer, Spark Notebook or Zepplin as a separate process. These programs are designed with their own infrastructure to allow external third parties to connect to them. End users can write thin-client applications connecting to these Spark Drivers.
Spark Submit is a terribly misnamed and overloaded function but it is simply put the only real supported way to run a Spark Application. It should be called “SparkApplicationLauncher” but Spark has many misnamed components (see Spark Master). In fact OSS Spark added a programatic api for running Spark Applications which is actually called Spark Launcher.
spark thrift server
https://www.russellspitzer.com/2017/05/19/Spark-Sql-Thriftserver/
Spark (SQL) Thrift Server is an excellent tool built on the HiveServer2 for allowing multiple remote clients to access Spark. It provides a generic JDBC endpoint that lets any client including BI tools connect and access the power of Spark.
介绍了一些spark的历史, 当年不少代码都是hive sql的代码, 后来引入了catalyst, 自己写了sql 解析器和执行计划, 替换了mr执行器, 然后慢慢的就从hive中独立出来了, 不少hive代码也都被挪走了.
Spark began replacing those various Hive-isms. Spark introduced a new representation for distributed tabular data, called SchemaRDDs Dataframes DataSets … naming is hard. And with that, a brand new Spark-native optimization engine known as Catalyst! Catalyst, a Tree Manipulation Framework, provided a basis for the query optimization present in everything from GraphFrames to Structured Streaming. The advent of Catalyst meant that old Map/Reduce-style execution could be dropped, and instead, Spark-optimized execution plans could be built and run.
以前的spark代码还需要选择HiveContext或者SqlContext, 现在都统一使用SparkSession.
Sql Thrift Server仍然基于hive server2开发, 不过里面的代码解析都是spark内置的了.
There was a short period in development where you had to pick between a HiveContext and SqlContext both of which had different parsers, but we don’t talk about that anymore. Today all requests start with a SparkSession. Now there is almost no Hive left in Spark. While the Sql Thrift Server is still built on the HiveServer2 code, almost all of the internals are now completely Spark-native.
Spark Contexts are also unable to share cached resources amongst each other. This means that unless you have a single Spark Context, it is impossible for multiple users to share a cached data. The Spark Thrift server can be that “single context,” providing globally-available cache.
这篇文章主要还是介绍 Spark Thrift Server的好处的, 主要是为了有一个统一的后台, 能够持续的提供spark服务, 而不是每一个spark application都单独提交占用一堆资源. 有了Spark Thrift Server, 客户端就可以直接通过jdbc进行sql查询调用了.
I’ve written about this before; Spark Applications are Fat. Each application is a complete self-contained cluster with exclusive execution resources. This is a problem if you want multiple users to share the same pool of cluster resources. The Spark Thrift Server provides a single context with a well-defined external protocol. This means external users can simultaneously send requests for Spark work without any Spark dependencies.
Spark Contexts are also unable to share cached resources amongst each other. This means that unless you have a single Spark Context, it is impossible for multiple users to share a cached data. The Spark Thrift server can be that “single context,” providing globally-available cache.
The Thrift Server can also benefit from Fair Scheduling. Fair Scheduling means that user requests do not have to be answered in a “First in, First out” manner. Instead, tasks from user queries can be interleaved. A long running query will not be able to block a shorter query from completing.
Additionally, the Thrift Server provides a greater level of Security by limiting the domain of jobs that a user can run. The Thrift Server prohibits running generic JVM code. Only SQL can be processed and executed.
Spark as cloud-based SQL Engine for BigData via ThriftServer
https://spoddutur.github.io/spark-notes/spark-as-cloud-based-sql-engine-via-thrift-server.html
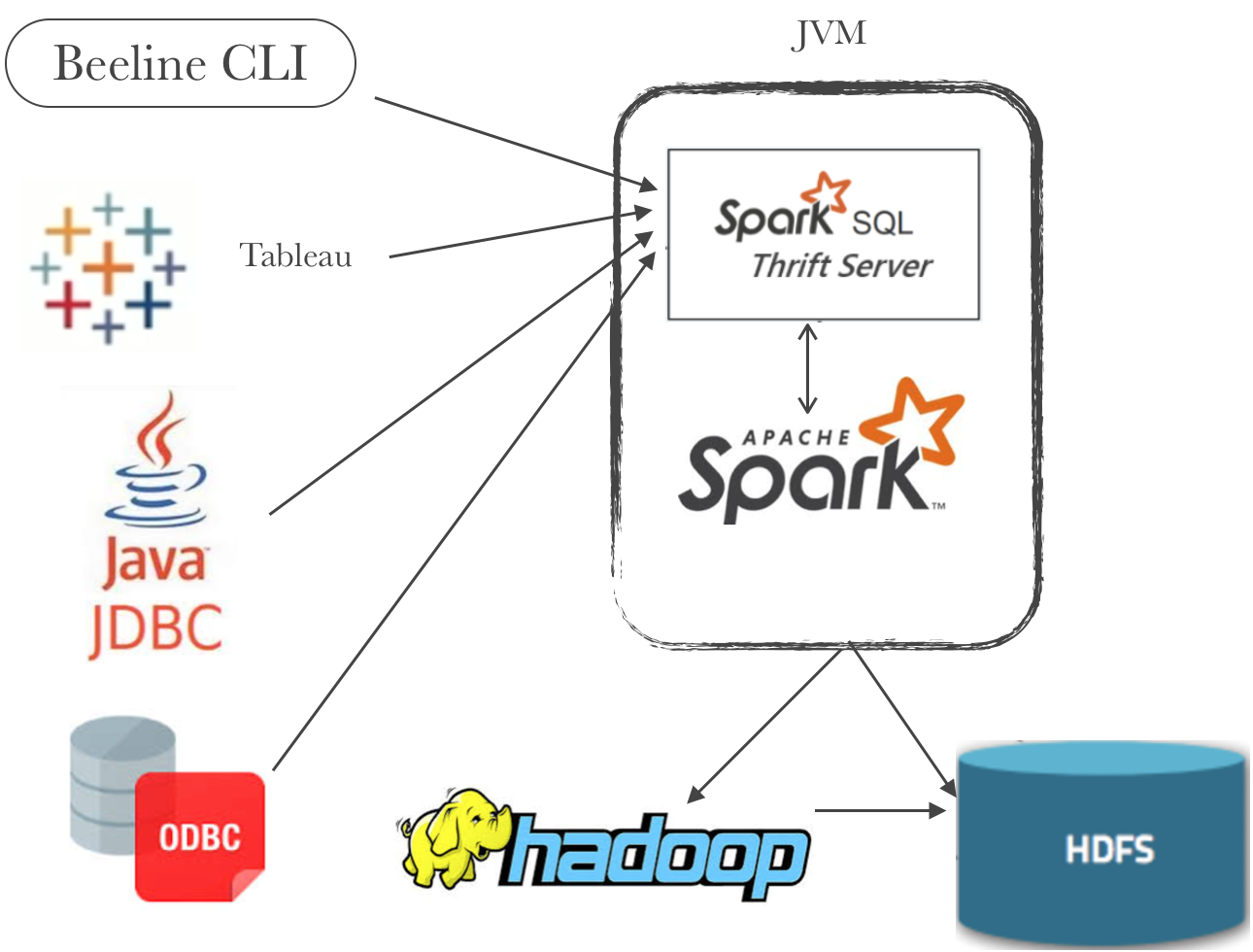
Spark thrift server is pretty similar to HiveServer2 thrift. But, HiveServer2 submits the sql queries as Hive MapReduce job whereas Spark thrift server will use Spark SQL engine which underline uses full spark capabilities.
hive server配置队列的方法
作为对比, hive server支持在连接jdbc字符串的时候配置hive队列
jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000?tez.queue.name=alt