kyuubi架构围观
看了一下kyuubi源码, 看了一些架构解读文章, 整体架构算是比较清楚了, 但是具体的细节实现其实还不清楚. 主要问题在于对spark本身没有那么熟悉, 其次对scala代码也不够熟悉.
一些杂七杂八的快速记录, 初步理解, 后面就得看具体实践和认知深入了.
kyuubi主要提供了一个统一的对外jdbc服务, 背后是kyuubi server, kyuubi server背后是spark engine, 也就是真正执行的spark应用.
具体细节里, 客户端driver连接, 首先访问的是kyuubi server端. kyuubi server本身是高可用架构, 具体链接哪个kyuubi server则是从zookeeper里选择决定的. kyuubi server接下来选择链接到背后的spark engine层, 根据connection的分享方式不同, 可以选择多个spark application, 或者同个用户共用spark application. 重点是kyuubi维持里这个spark application, 不需要由spark thrift server提供长期的服务, 也不需要每次单独漫长的启动spark application. 在间隔空闲时间到了之后, 自动关闭spark application. 通过每次单独维护或者启动spark application, kyuubi实现了spark应用的资源分配和用户识别, 也因此实现了所谓的多租户和资源隔离的功能.
原来的spark thrift server被诟病的地方,主要是本质上只是一个spark application应用, 所使用的用户, 使用的yarn/k8s资源在启动的时候就确定了, 没法修改. 所以spark thrift server对外提供的jdbc服务, 并不能有效隔离用户, 只是提供了一个统一对外jdbc sql访问执行的服务. spark thrift server本身来自hive thrift server, 也就是hive server2, 不过只是用了个框架, 里面基本上替换成了spark的功能, 比如sql解析和具体执行.
hive server本身是支持多租户和资源配置的, 每个连接到hive server的jdbc都可以配置yarn队列, 也可以配置用户身份信息, hive server在解析后, 具体的执行会继续交给背后的mr, teg或是spark(hive on spark). spark thrift server也是thrift server, 估计不支持多租户和资源配置的原因, 估计是本身只是一个已经启动的spark applictation, 导致反而无法随时切换了.
spark thrift application本身对spark也是一个不错的贡献. 因为普通的spark任务都需要通过spark submit提交, spark submit又是一个fat应用, 依赖特别多, 启动和分配速度比较缓慢. 使用spark thrift server, 后台就不用重复启动了, 并且也提供了一个可以给外部直接通过jdbc链接的地方. spart thrift server需要在安装spark的时候进行独立配置启动.
另外spark thrift application里也支持ranger的hive sql配置.
其实还有一个问题, hive on spark也是spark, 也对外提供hive jdbc服务, 也支持多租户和资源配置, 其实大多数场景已经满足需求了吧?
官方架构文档
Kyuubi Architecture
https://kyuubi.readthedocs.io/en/v1.6.0-incubating/overview/architecture.html
整体架构
kyuubi提供了一个统一的对外jdbc服务
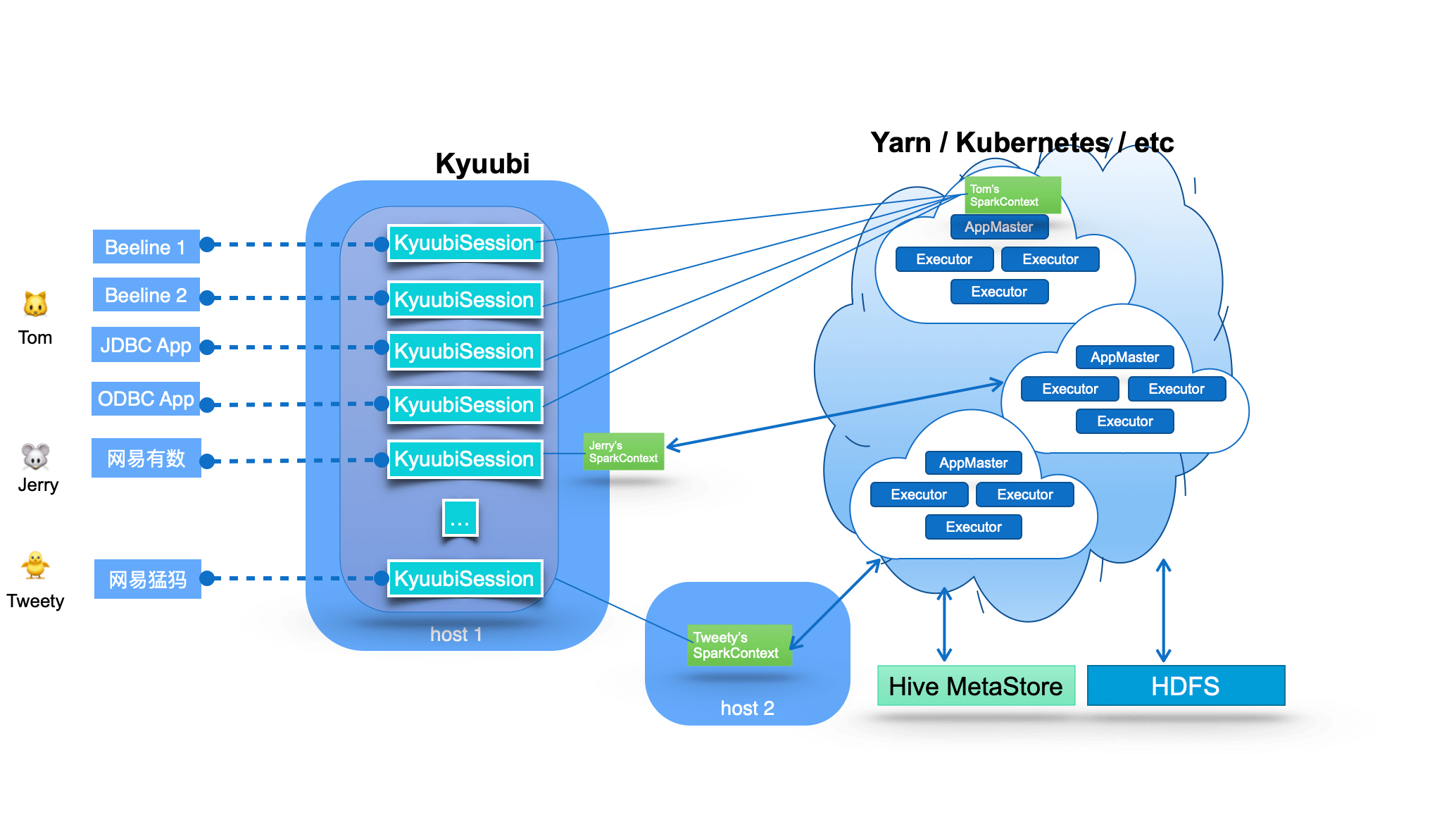
中间的kyuubi session并不是spark session, 属于kyuubi server 接受jdbc请求时提供的session管理. spark context则是远程的spark执行程序, 通过kyuubi service启动管理.
These SparkConexts instances are essentially remote query execution engine programs hosted by Kyuubi services. These programs are implemented on Spark SQL and compile, optimize, and execute SQL statements end-to-end and the necessary interaction with the metadata (e.g. Hive Metastore) and storage (e.g. HDFS) services, maximizing the power of Spark SQL. They can manage their lifecycle, cache and recycle themselves, and are not affected by failover on the Kyuubi server.
资源分配 Runtime Resource Resiliency
kyuubi支持连接jdbc的时候, 通过配置queue队列信息管理分配的资源
The most significant difference between Kyuubi and Spark Thrift Server(STS) is that STS is a single Spark application. For example, if it runs on an Apache Hadoop Yarn cluster, this application is also a single Yarn application that can only exist in a specific fixed queue of the Yarn cluster after it is created. Yarn loses its role as a resource manager for resource management and does not play the corresponding role of resource isolation and sharing. When users from the client have different resource queue permissions, STS will not be able to handle it in this case.
Kyuubi creates different Spark applications based on the connection requests from the client, and these applications can be placed in different shared domains for other connection requests to share.
./beeline -u "jdbc:hive2://kyuubi.org:10009/;\
hive.server2.proxy.user=tom#\
spark.yarn.queue=thequeue;\
spark.dynamicAllocation.enabled=true;\
spark.dynamicAllocation.maxExecutors=500;\
spark.shuffle.service.enabled=true;\
spark.executor.cores=3;\
spark.executor.memory=10g"
高可用架构
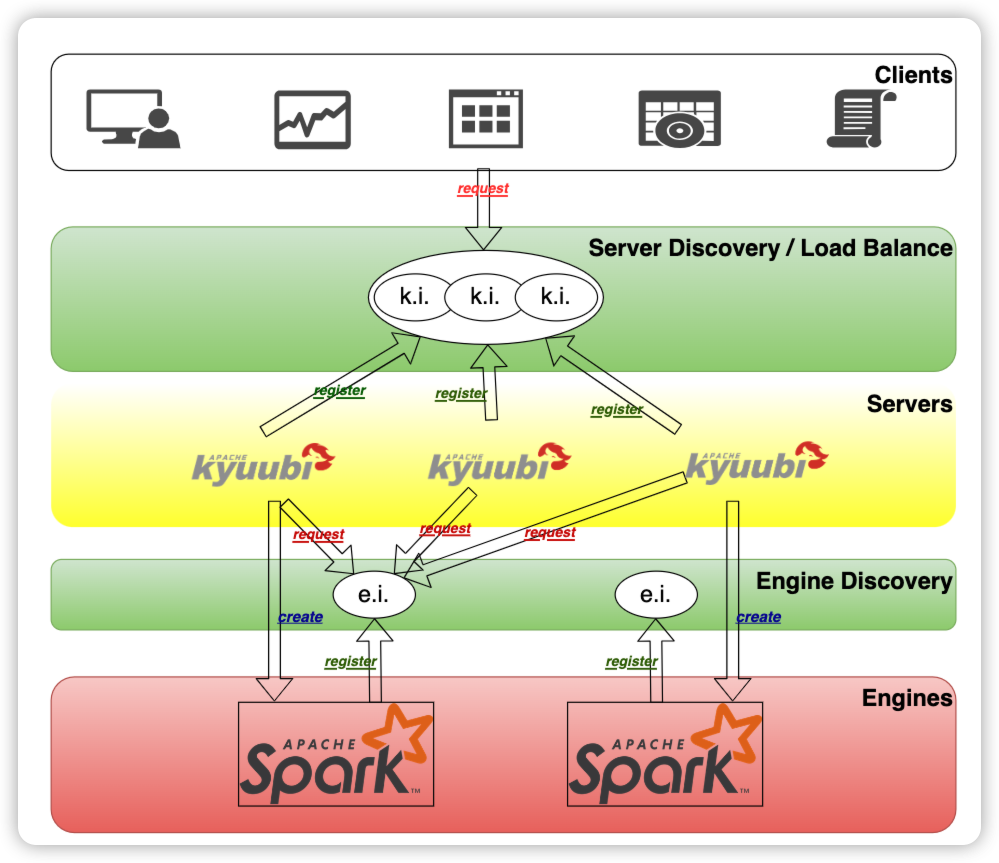
用户客户端通过jdbc连接kyuubi的时候, 通过zookeeper返回kyuubi server的地址. kyuubi server分配spark engine的时候, 也是通过zookeeper去查找是否有可用的spark engine信息, 如果有则复用, 没有则按需创建.

- At the top of the diagram is the client layer. A client can find multiple registered instances of Kyuubi instance (k.i.) from the namespace in the service discovery layer and then choose to connect. Kyuubi instances registered to the same namespace provide the ability to load balance each other.
- The selected Kyuubi instance will pick an available engine instance (e.i.) from the engine-namespace in the service discovery layer to establish a connection. If no available instance is found, it will create a new one, wait for the engine to finish registering, and then proceed to connect.
- If the same person requests a new connection, the connection will be set up to the same or another Kyuubi instance, but the engine instance will be reused.
- For connections from different users, the step 2 and 3 will be repeated. This is because in the service discovery layer, the namespaces used to store the address of the engine instances are isolated based on the user(by default), and different users cannot access other’s instances across the namespace.
认证鉴权 Authentication & Authorization
认证方面支持kerberos, kyuubi本身有server principal, 创建spark engine的时候支持传递用户的信息.
鉴权支持通过spark authz ranger插件. 鉴权插件本身作用在spark层, 在spark执行sql解析的时候进行拦截.
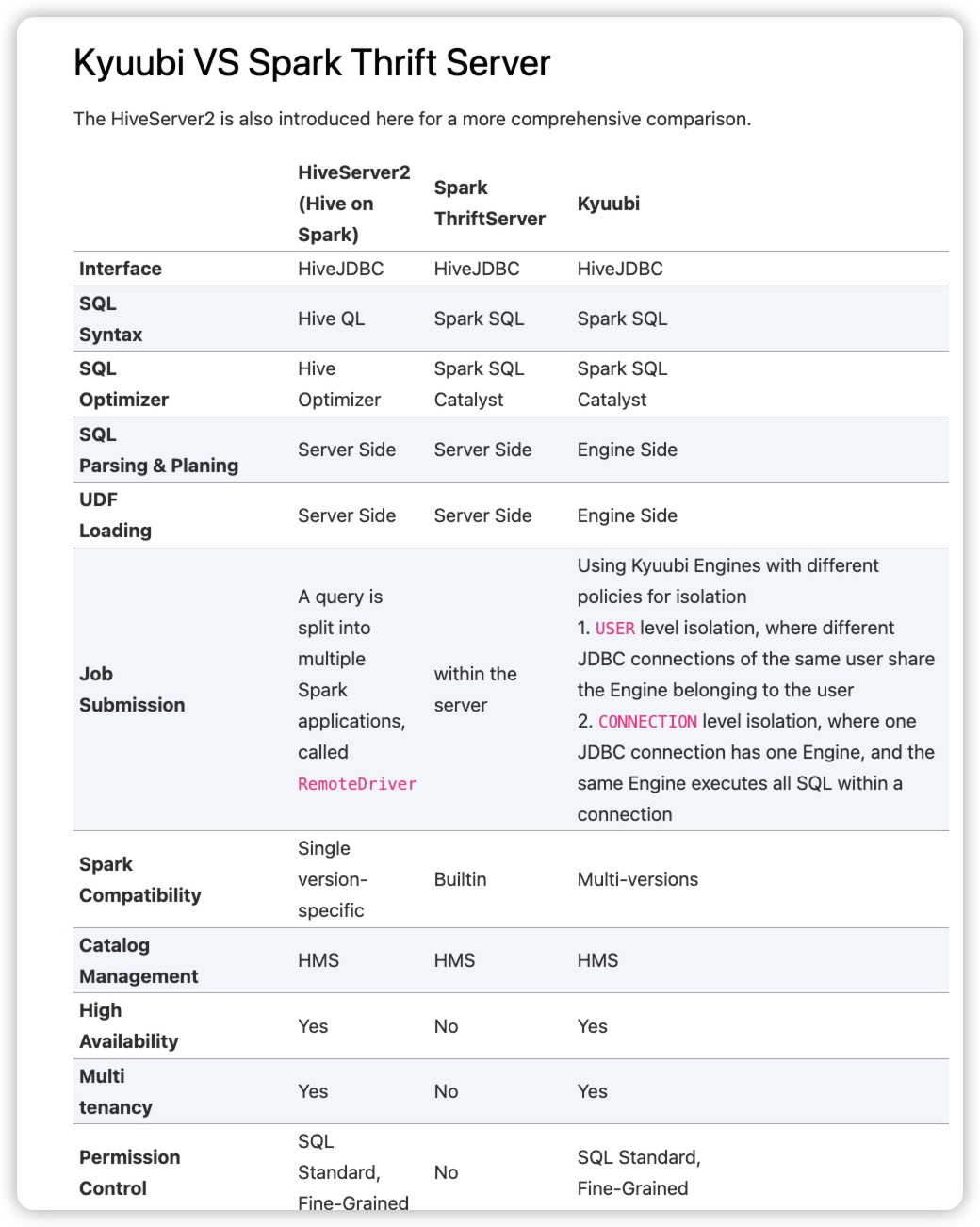
kyuubi 对比spark thrift server
Kyuubi v.s. Spark Thrift JDBC/ODBC Server (STS)
https://kyuubi.readthedocs.io/en/v1.6.0-incubating/overview/kyuubi_vs_thriftserver.html
kyuubi的session维护图
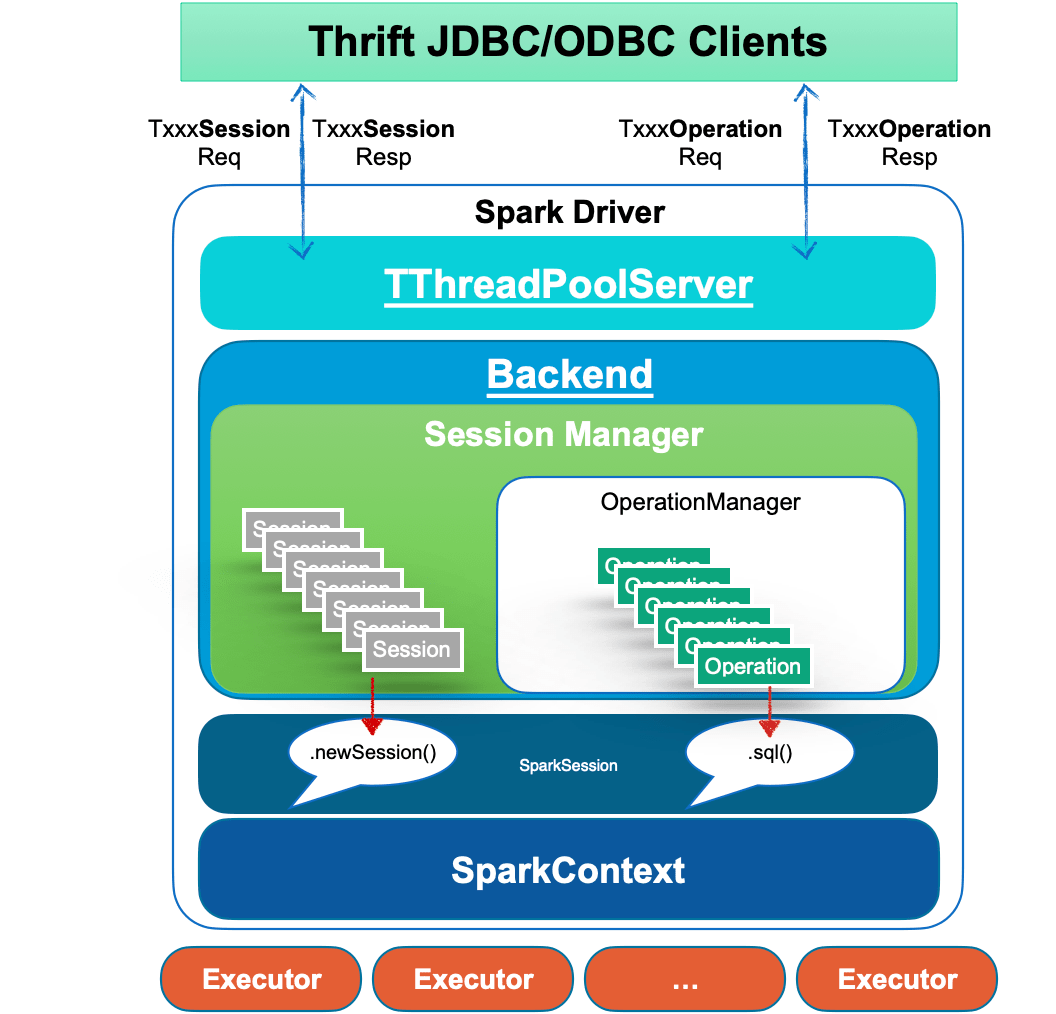
The JDBC connections and operations are handled by the frontend thread pool as various requests. And the corresponding methods of the backend are called to bind to the SparkSession related interface. For example, the DriverManager.getConnection at the client-side will invoke SparkSession.newSession() at the server-side, and all queries from the client-side will be submitted to the backend thread pool asynchronously and executed by SparkSession.sql(...).
普通的spark应用是fat应用, 自身需要包含所有依赖和配置, 因此需要暴露spark/hive xml等一些配置信息给用户. 而kyuubi的各种spark配置都在kyuubi server端, 因此连接kyuubi jdbc的用户不需要去关注.
Secondly, all the setups for backend services, such as YARN, HDFS, and Hive Metastore Server(HMS), are completed in Spark ThriftServer, so there is no need to hand over the configuration of the backend services to the end-users.
Kyuubi v.s. HiveServer2
https://kyuubi.readthedocs.io/en/v1.6.0-incubating/overview/kyuubi_vs_hive.html
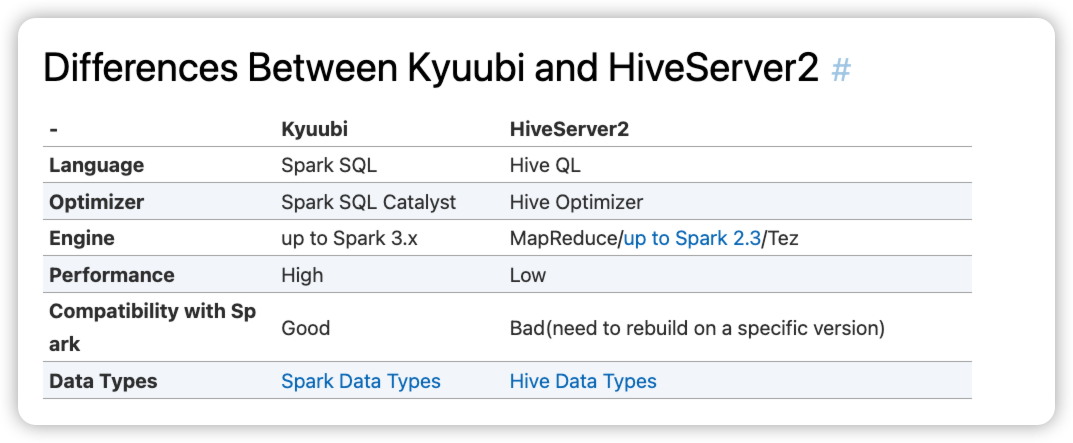
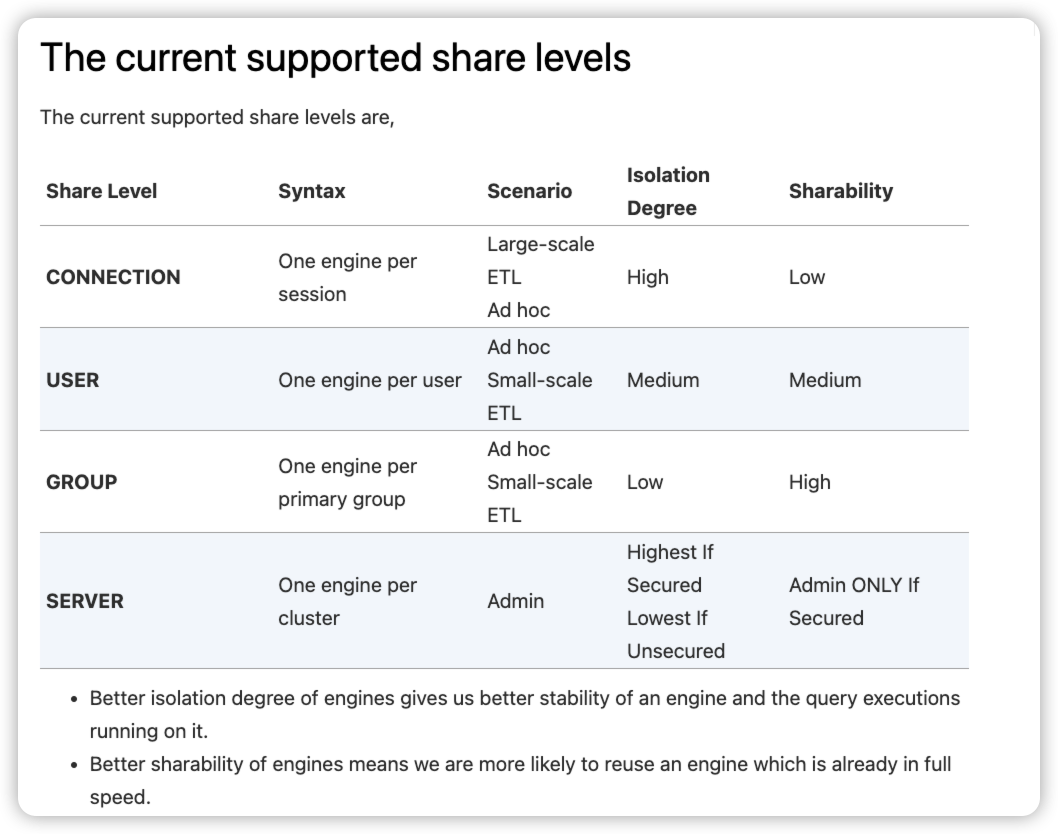
kyuubi 隔离级别
sparksession可以提供给多个jdbc连接使用, 后台等同于维持里一个连接线程池.
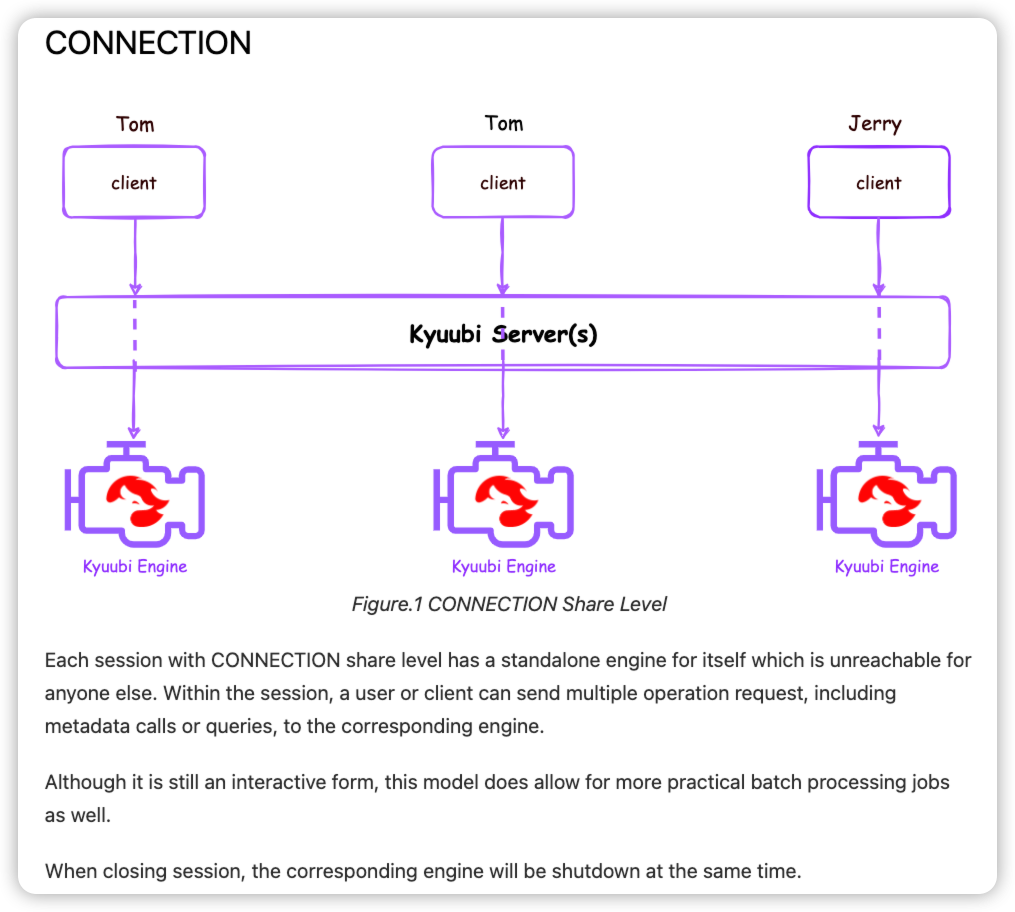
conneciton级别, 每个jdbc连接都重新启动一个spark context. 适合比较重的etl服务, 没有资源共享.
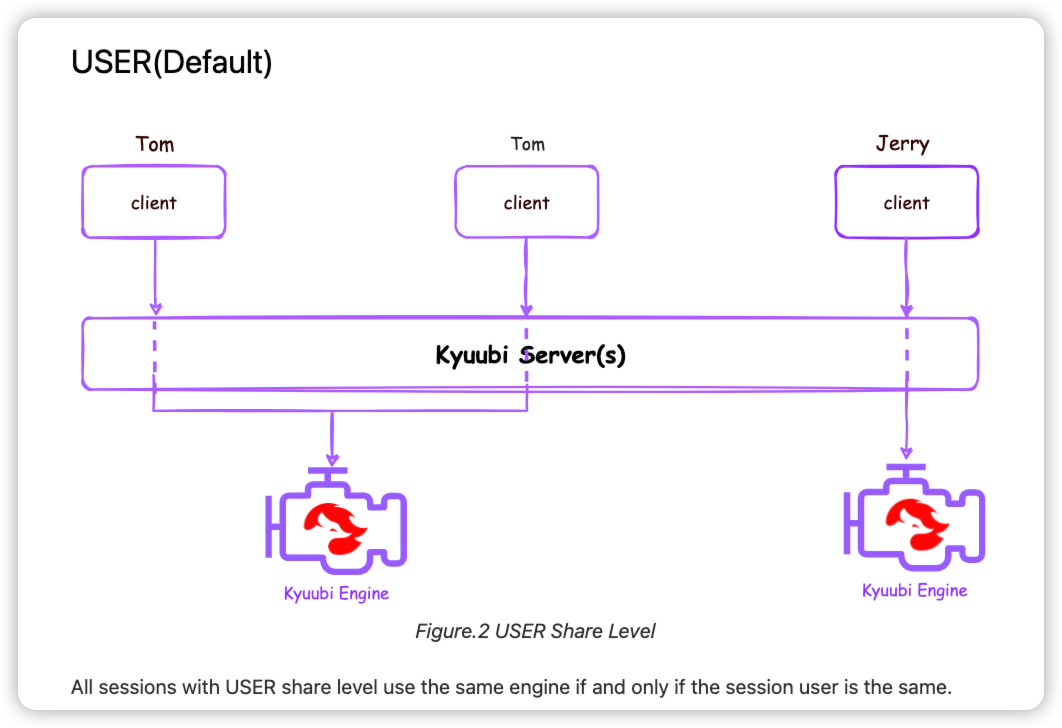
默认的user级别, 同个用户的连接会共享
server隔离层级, 等同于一个spark thrift server
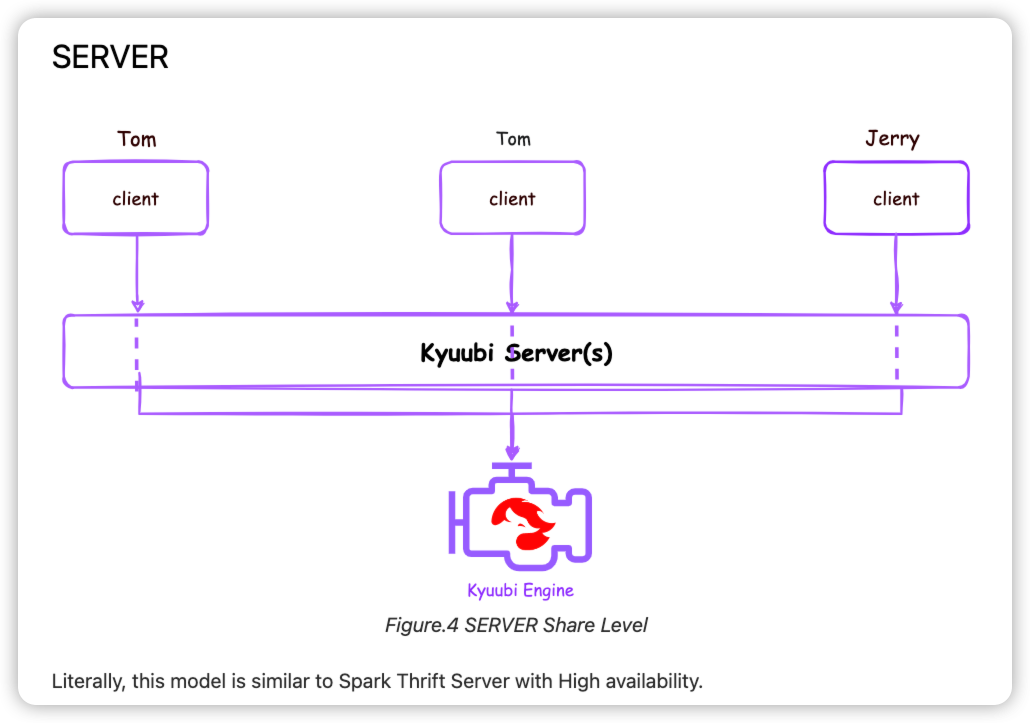
博客围观
网易Spark Kyuubi核心架构设计与源码实现剖析
https://blog.51cto.com/xpleaf/2780248
这篇博客讲得非常详细, kyuubi主要架构和代码都有涉及, 看源码的时候结合查看能减少不少困惑点.
博客作者的感慨很有道理: 不管对于哪个大数据组件,在理解了其底层通信框架的基础上,再选取关于该组件的几个或多个关键场景来分析其源码,基本上对其整体设计就会有概览性的理解,这样后面对于该组件可能出现的Bug进行排查与修复,或是对该组件进行深度定制以满足业务的实际需求,我相信问题都不大.
Kyuubi的整体架构设计如下:
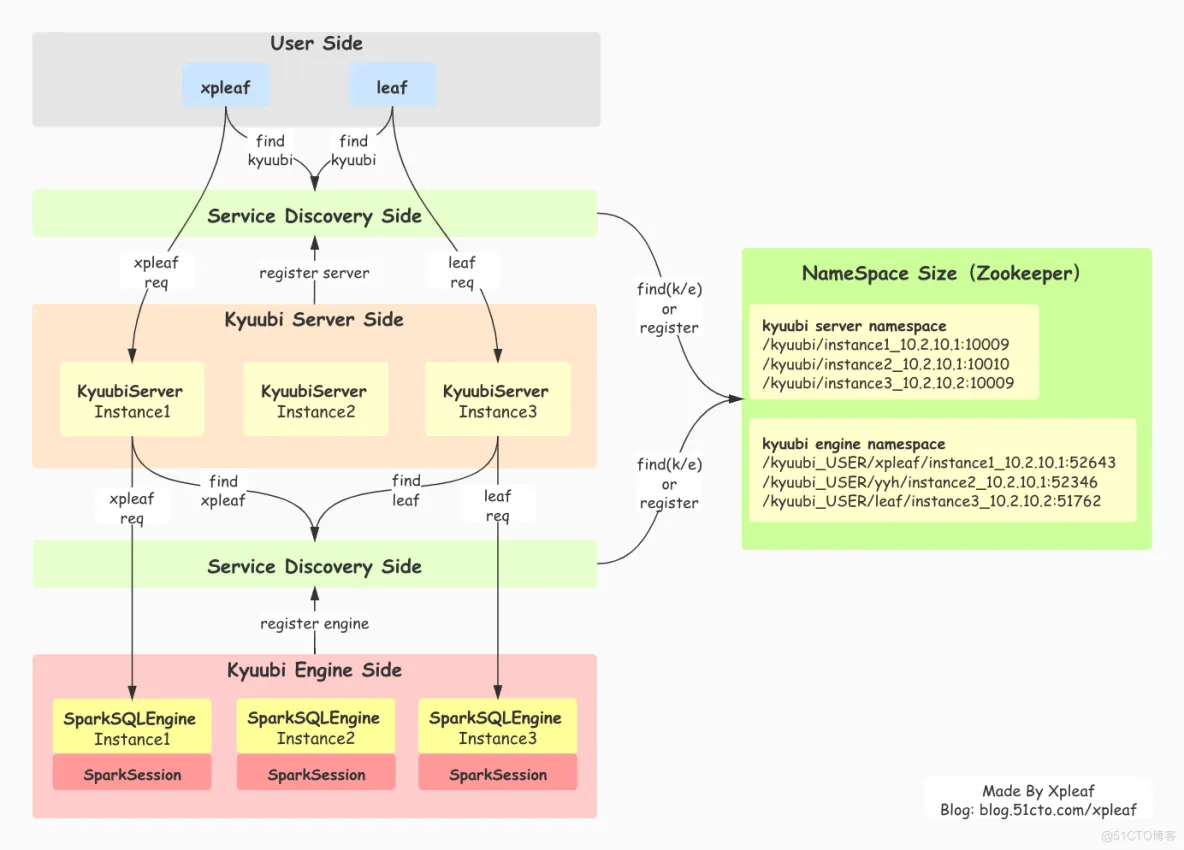
Kyuubi从整体上可以分为用户层、服务发现层、Kyuubi Server层、Kyuubi Engine层,其整体概述如下:
用户层 指通过不同方式使用Kyuubi的用户,比如通过JDBC或beeline方式使用Kyuubi的用户。
服务发现层 服务发现层依赖于Zookeeper实现,其又分为Kyuubi Server层的服务发现和Kyuubi Engine层的服务发现。
Kyuubi Server层 由多个不同的KyuubiServer实例组成,每个KyuubiServer实例本质上为基于Apache Thrift实现的RPC服务端,其接收来自用户的请求,但并不会真正执行该请求的相关SQL操作,只会作为代理转发该请求到Kyuubi Engine层用户所属的SparkSQLEngine实例上。
Kyuubi Engine层 由多个不同的SparkSQLEngine实例组成,每个SparkSQLEngine实例本质上为基于Apache Thrift实现的并且持有一个SparkSession实例的RPC服务端,其接收来自KyuubiServer实例的请求,并通过SparkSession实例来执行。在Kyuubi的USER共享层级上,每个SparkSQLEngine实例都是用户级别的,即不同的用户其会持有不同的SparkSQLEngine实例,以实现用户级别的资源隔离和控制。
Apache Kyuubi 在B站大数据场景下的应用实践
没想到b站内部还做了这么多改造, 看起来工作量也是巨大. 内部大数据系统真是一顿瞎搞, 每个公司都搞一遍, 程序员人力真多啊.
https://www.cnblogs.com/163yun/p/16833191.html
随着B站业务高速发展,离线计算集群规模从最初的两百台发展到目前近万台,从单机房发展到多机房架构。在离线计算引擎上目前我们主要使用Spark、Presto、Hive。架构图如下所示,我们的BI、ADHOC以及DQC服务都是通过自研的Dispatcher路由服务来实现统一SQL调度,Dispatcher会结合查询SQL语法特征、读HDFS量以及当前引擎的负载情况,动态地选择当前最佳计算引擎执行任务。如果用户SQL失败了会做引擎自动降级,降低用户使用门槛;其中对于Spark查询早期我们都是走STS,但是STS本身有很多性能和可用性上的问题,因此我们引入了Kyuubi,通过Kyuubi提供的多租户、多引擎代理以及完全兼容Hive Thrift协议能力,实现各个部门Adhoc任务的资源隔离和权限验证。
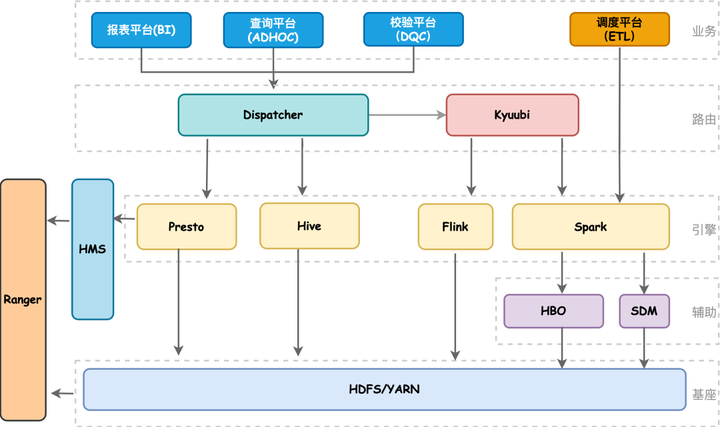
B站估计把user group当作项目进行管理, 实现了同一个项目的人员使用相同yarn队列的分配管理.
Kyuubi Engine原生提供了CONNECTION、USER、GROUP和SERVER多种隔离级别。在B站大数据计算资源容量按照部门划分,不同部门在Yarn上对应不同的队列。基于GROUP模式进行了改造,实现Queue级别的资源隔离和权限控制。
用户信息和队列的映射由上层工具平台统一配置和管理,Kyuubi只需关心上游Dispatcher提交过来user和queue信息,进行调度并分发到对应队列的spark engine上进行计算。目前我们有20+个adhoc队列,每个队列都对应一个或者多个Engine实例(Engine pool)。
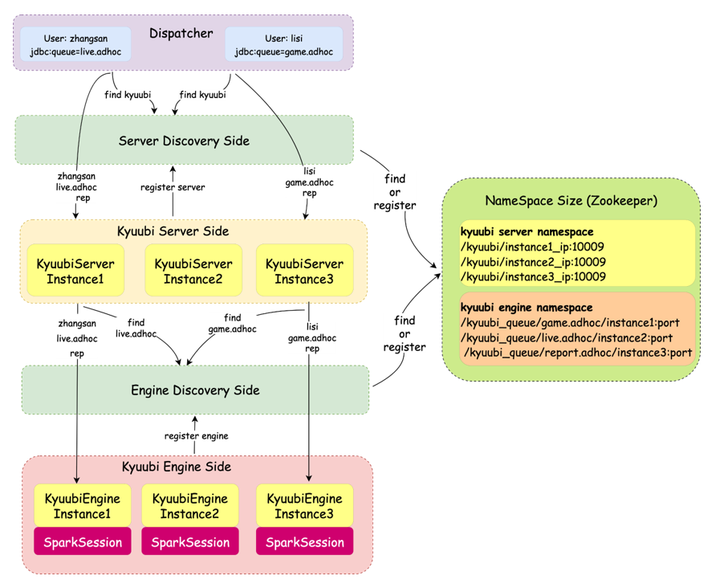
kyuubi server端由超级用户Hive启动,在spark场景下driver和executor共享同一个的用户名。不同的用户提交不同的sql, driver端和executor端无法区分当前的任务是由谁提交的,在数据安全、资源申请和权限访问控制方面都存在着问题。