netty 入个门
dolphin-scheduler里面, master和worker的交互并不是通过http server, 而是通过netty server, 这里顺便了解下netty的用法.
spring webflux的底层也是netty server.
netty
netty 官方介绍
Netty is an asynchronous event-driven network application framework for rapid development of maintainable high performance protocol servers & clients.
Netty is an NIO client server framework which enables quick and easy development of network applications such as protocol servers and clients. It greatly simplifies and streamlines network programming such as TCP and UDP socket server.
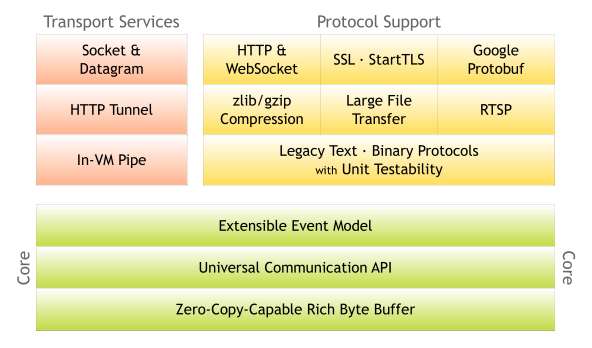
A Quick Guide to Java on Netty
看下demo, 对如何使用就有大概的概念了. 有些配置都是常规的, 关键的其实只有handler的写法.
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2019/11/25/java-netty-webflux#secure-your-app-with-oauth-20
First, take a look at the src/main/java/com/okta/netty/AppServer.java file. This class is the entry point for the application and sets up the Netty server.
package com.okta.netty;
...
public class AppServer {
private static final int HTTP_PORT = 8080;
public void run() throws Exception {
// Create the multithreaded event loops for the server
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// A helper class that simplifies server configuration
ServerBootstrap httpBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
// Configure the server
httpBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ServerInitializer()) // <-- Our handler created here
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
// Bind and start to accept incoming connections.
ChannelFuture httpChannel = httpBootstrap.bind(HTTP_PORT).sync();
// Wait until server socket is closed
httpChannel.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}
finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new AppServer().run();
}
}
The most important line is .childHandler(new ServerInitializer()), which creates ServerInitializer and ServerHandler and hooks into the Netty server.
Next look at src/main/java/com/okta/netty/ServerInitializer.java. This class configures the Netty channel that will handle our requests and connects it to the ServerHandler.
package com.okta.netty;
...
public class ServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
pipeline.addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
}
Finally, there is src/main/java/com/okta/netty/ServerHandler.java. This is where the actual request is mapped and the response is generated.
package com.okta.netty;
...
public class ServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest msg) {
ByteBuf content = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello World!", CharsetUtil.UTF_8);
FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, content);
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html");
response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH, content.readableBytes());
ctx.write(response);
ctx.flush();
}
}
$ http :8080
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
content-length: 12
content-type: text/html
Hello World!
webflux demo
by default, the Spring Boot WebFlux starter runs on a Netty server.
Take a look at the ReactiveApplication class. It’s the bare-bones, standard Spring Boot application class. It simply leverages the public static void main() method and the @SpringBootApplication to start the whole Spring Boot application framework.
src/main/java/com/okta/webflux/app/ReactiveApplication.java
package com.okta.webflux.app;
...
@SpringBootApplication
public class ReactiveApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ReactiveApplication.class, args);
}
}
The ReactiveRouter is a simple router class that links HTML endpoints with handler methods. You can see that it uses dependency injection to pass the ReactiveHandler to the router bean, which defines a single endpoint for the / route.
src/main/java/com/okta/webflux/app/ReactiveRouter.java
package com.okta.webflux.app;
...
@Configuration
public class ReactiveRouter {
@Bean
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route(ReactiveHandler handler) {
return RouterFunctions
.route(RequestPredicates
.GET("/")
.and(RequestPredicates.accept(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)), handler::hello);
}
}
The ReactiveHandler is similarly simple. It defines one handler function that returns plain text. The Mono<ServerResponse> return type is a special type for returning a stream of one element. Take a look at the Spring Docs on Understanding Reactive types to learn more about return types. If you’re used to Spring MVC, this will likely be one of the more unfamiliar aspects of WebFlux.
package com.okta.webflux.app;
...
@Component
public class ReactiveHandler {
public Mono<ServerResponse> hello() {
return ServerResponse
.ok()
.contentType(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN)
.body(BodyInserters.fromObject("Hello world!"));
}
}
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 12
Content-Type: text/plain
Hello world!
Building a simple Netty server and client
https://medium.com/@cjz.lxg/building-a-simple-netty-server-and-client-d95061156313
这个例子展示了server和客户端都使用netty进行交互的场景
- server side
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
public class EchoServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap()
.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
static class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
ctx.write(msg);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
}
- client side
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class EchoClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
static class EchoClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf message = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello, Netty!", StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println("Received from server: " + byteBuf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
byteBuf.release();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
}
Run the EchoServer class first, and then run the EchoClient class. The server will listen on port 8080, and the client will connect to it. The client sends a "Hello, Netty!" message, and the server will echo it back to the client. The client will print the received message to the console.
dolhpin scheduler 的 netty server
public void start() {
if (isStarted.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
this.serverBootstrap
.group(this.bossGroup, this.workGroup)
.channel(NettyUtils.getServerSocketChannelClass())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, serverConfig.getSoBacklog())
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, serverConfig.isSoKeepalive())
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, serverConfig.isTcpNoDelay())
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, serverConfig.getSendBufferSize())
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, serverConfig.getReceiveBufferSize())
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
initNettyChannel(ch);
}
});
ChannelFuture future;
try {
future = serverBootstrap.bind(serverConfig.getListenPort()).sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("{} bind fail {}, exit", serverConfig.getServerName(), e.getMessage(), e);
throw new RemoteException(
String.format("%s bind %s fail", serverConfig.getServerName(), serverConfig.getListenPort()));
}
if (future.isSuccess()) {
log.info("{} bind success at port: {}", serverConfig.getServerName(), serverConfig.getListenPort());
return;
}
if (future.cause() != null) {
throw new RemoteException(
String.format("%s bind %s fail", serverConfig.getServerName(), serverConfig.getListenPort()),
future.cause());
} else {
throw new RemoteException(
String.format("%s bind %s fail", serverConfig.getServerName(), serverConfig.getListenPort()));
}
}
}
handler 转发逻辑
initNettyChannel(ch)
private void initNettyChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline()
.addLast("encoder", new TransporterEncoder())
.addLast("decoder", new TransporterDecoder())
.addLast("server-idle-handle",
new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, Constants.NETTY_SERVER_HEART_BEAT_TIME, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
.addLast("handler", serverHandler);
}
public void registerMethodInvoker(ServerMethodInvoker methodInvoker) {
checkNotNull(methodInvoker);
checkNotNull(methodInvoker.getMethodIdentify());
methodInvokerMap.put(methodInvoker.getMethodIdentify(), methodInvoker);
}
注册函数方法的入口
@Nullable
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Class<?>[] interfaces = bean.getClass().getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> anInterface : interfaces) {
if (anInterface.getAnnotation(RpcService.class) == null) {
continue;
}
registerRpcMethodInvoker(anInterface, bean, beanName);
}
return bean;
}
private void registerRpcMethodInvoker(Class<?> anInterface, Object bean, String beanName) {
Method[] declaredMethods = anInterface.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : declaredMethods) {
RpcMethod rpcMethod = method.getAnnotation(RpcMethod.class);
if (rpcMethod == null) {
continue;
}
ServerMethodInvoker methodInvoker = new ServerMethodInvokerImpl(bean, method);
nettyRemotingServer.registerMethodInvoker(methodInvoker);
log.debug("Register ServerMethodInvoker: {} to bean: {}", methodInvoker.getMethodIdentify(), beanName);
}
}
所以其实是有@RpcService和@RpcMethod的, 才会被添加到netty server handler里进行转发.
比如worker的交互
package org.apache.dolphinscheduler.extract.worker;
import org.apache.dolphinscheduler.extract.base.RpcMethod;
import org.apache.dolphinscheduler.extract.base.RpcService;
import org.apache.dolphinscheduler.extract.worker.transportor.TaskInstanceExecutionFinishEventAck;
import org.apache.dolphinscheduler.extract.worker.transportor.TaskInstanceExecutionInfoEventAck;
import org.apache.dolphinscheduler.extract.worker.transportor.TaskInstanceExecutionRunningEventAck;
@RpcService
public interface ITaskInstanceExecutionEventAckListener {
// todo: If we use sync, then we don't need ack here
@RpcMethod
void handleTaskInstanceExecutionRunningEventAck(TaskInstanceExecutionRunningEventAck taskInstanceExecutionRunningEventAck);
@RpcMethod
void handleTaskInstanceExecutionFinishEventAck(TaskInstanceExecutionFinishEventAck taskInstanceExecutionFinishEventAck);
@RpcMethod
void handleTaskInstanceExecutionInfoEventAck(TaskInstanceExecutionInfoEventAck taskInstanceExecutionInfoEventAck);
}