从 hive-hdfs 看大数据领域鉴权问题
看了一圈各种大数据组件的鉴权方案, 就能意识到一个问题,大数据鉴权这个领域目前是没完没了, 没有完美方案能够覆盖各种大数据组件组合的场景. 主要的根源是大数据新组件的研发初衷, 一般都是为了提供更快的计算速度, 更多的分析功能, 就没听说为了提供更高安全性的. 设计前期基本上是不会考虑鉴权问题的, 如果提前考虑了用户的授权鉴权问题, 引入额外的业务逻辑代码, 反而会拖累整个组件的运算速度. 所以一般得等到新组件已经打出一片天地了, 有一堆公司在使用了, 才会来修修补补的考虑鉴权问题. 比如一开始的hdfs/hive就没有认证和鉴权, 后来认证通过kerberos补上了, 鉴权慢慢也由ranger/sentry/acl等补上了, 但是目前两者的搭配还是容易出现各种问题.
对于大公司而言, 使用各种大数据组件组合, 会发现到处都是补不上的鉴权漏洞. 每个组件可能都有自己的一套鉴权流程, 但也都容易被另一个组件给突破了. 对于提供各种访问方法的大数据平台而言, 问题更加复杂了. 比如如果能够限制用于只使用hive sql, 那么ranger hive已经能够很好覆盖授权需求. 如果要支持某些场景下用户直接操作hdfs, 那就同时需要考虑 hdfs 权限问题, hdfs ranger开始浮出水面. 此时考虑了hdfs鉴权, 对于hive sql而言, 就不只是需要考虑hive sql 库表权限问题, 还需要考虑与hdfs权限的联动. 当然这种也有很多种方案, 比如在配置hive的时候, 根据hive table的location配置对应的hdfs路径; 比如配置hive操作的doAs为false, 由hive主账号去操作hdfs; 比如修改ranger鉴权代码逻辑, 在判断hdfs权限的时候, 直接检查路径是否有hive权限. 但这里面又会遇到各种细节问题, 比如hive view的权限问题, 比如hive的column 字段权限问题, 比如内外表的路径问题, hive 与hdfs 之间的配合总有些边角问题. 当考虑完hive/hdfs这些问题了, 如果支持用户直接使用spark, 就会发现spark可以直接绕过hive的权限认证. 因为spark可以配置只读取hive metastore, 不通过hive server2. 这时候要考虑如何限制sparksql, 接下来就要考虑spark jar是否要限制? 考虑完spark权限问题, 会发现还有presto权限问题. 考虑完presto权限问题, 会发现不只sql引擎计算层需要考虑, 存储层的hdfs可能修改为ozone存储, alluxio存储, 甚至云上的cos/s3存储, 又是一堆需要考虑的问题.
在堵上每种组件的漏洞后, 对于大数据治理平台而言并不代表着结束, 因为在授权的时候, 需要让用户的授权操作自洽且丝滑. 不能够让用户建一个表, 要申请hive权限, 还要自己去申请对应的hdfs路径权限, 甚至还要用户考虑去授权hdfs父级路径的权限(因为有父目录权限才能创建子文件). 因此这不只是考虑某个组件单一访问场景的问题, 还要考虑在各种组合下, 权限系统都能够限制用户的操作, 并且授权鉴权过程都是丝滑体验.
综上, 这个领域坑太多了, 每个大一点的公司都在摸索, 打工人不停的重复搬砖. 看一下hive的官方文档会发现早有答案, 放弃完美主义, 只考虑某些业务场景, 从业务上进行限制, 自行取舍. 比如hive的sql base storage authorization方案架构文档里, 就直接说在sql授权方案的领域, 不考虑直接读取hdfs的用户, 这些不属于数据分析师范围.
再来一些建议, 尽量把关键的组件的源码看了, 比如ranger的, hive的, hdfs的, 这样比杂七杂八看文章看博客理解深刻多了. 看文档也建议把hive/cdh/ibm的官方文档看了, 高屋建瓴的官方文档比杂七杂八的博客文档水平高多了, 很多早就在官方组件的设计文档里提供了解决方法了. 最后就是多测试, 执行看权限拦截报错, 才知道具体是怎么回事.
这个领域里的很多问题早就被讨论过无数遍了, 可怜的打工人还要一遍遍重复摸索重复搬砖. 不如看源码去...
HCatalog Authorization
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/HCatalog+Authorization
2018年的文章, 放弃了hive授权的“银弹” 完美主义, 提供各种插件来满足各种需求.
The Hive community realizes that there might not be a one-size-fits-all authorization model, so it has support for alternative authorization models to be plugged in.
In the HCatalog package, we have introduced implementation of an authorization interface that uses the permissions of the underlying file system (or in general, the storage backend) as the basis of permissions on each database, table or partition.
SQL Standard Based Hive Authorization
2018年的文章, 针对使用场景考虑授权问题, sql 授权只考虑jdbc连接的数据分析师, 不考虑使用spark的etl用户.
Under this authorization model, users who have access to the Hive CLI, HDFS commands, Pig command line, 'hadoop jar' command, etc., are considered privileged users. In an organization, it is typically only the teams that work on ETL workloads that need such access. These tools don't access the data through HiveServer2, and as a result their access is not authorized through this model. For Hive CLI, Pig, and MapReduce users access to Hive tables can be controlled using storage based authorization enabled on the metastore server.
Most users such as business analysts tend to use SQL and ODBC/JDBC through HiveServer2 and their access can be controlled using this authorization model.
hive 授权定义
LanguageManual Authorization
2019年的文章, 高屋建瓴的提供了hive鉴权的思路和方案.
hive有两种需要不同鉴权的使用场景:
把hive当作元数据的库表存储, 主要使用hive的HCatalog API进行操作, 比如spark, imapla, presto等. 这些组件能够直接读取hdfs, 对于hive则只操作metadata api. 这些类型可以使用storage base authorization. hive的metastore里也保存了hdfs路径, 支持从metastore之间鉴权hdfs.
把hive当作sql插叙引擎使用, 这些用户基本都通过hive server api进行交互, 可以使用sql鉴权. hive cli 由于可以直接读取hdfs, 也不支持鉴权, 相对而言 beeline 支持.
It is useful to think of authorization in terms of two primary use cases of Hive.
Hive as a table storage layer. This is the use case for Hive's HCatalog API users such as Apache Pig, MapReduce and some Massively Parallel Processing databases (Cloudera Impala, Facebook Presto, Spark SQL etc). In this case, Hive provides a table abstraction and metadata for files on storage (typically HDFS). These users have direct access to HDFS and the metastore server (which provides an API for metadata access). HDFS access is authorized through the use of HDFS permissions. Metadata access needs to be authorized using Hive configuration.
Hive as a SQL query engine. This is one of the most common use cases of Hive. This is the 'Hive view' of SQL users and BI tools. This use case has the following two subcategories: a. Hive command line users. These users have direct access to HDFS and the Hive metastore, which makes this use case similar to use case 1. Note, that usage of Hive CLI will be officially deprecated soon in favor of Beeline. b. ODBC/JDBC and other HiveServer2 API users (Beeline CLI is an example). These users have all data/metadata access happening through HiveServer2. They don't have direct access to HDFS or the metastore.
hive storage based authorization
对于直接读取hive metastore 然后操作hdfs的用户, hive提供了storaged based authorization, 看文档像是对metastore进行操作的时候, 就会去判断用户在hdfs里的权限? 没有去测试过, 以前以为是交给hdfs授权单独拦截了, 不知道metastore是否有联动?
In use cases 1 and 2a, the users have direct access to the data. Hive configurations don't control the data access. The HDFS permissions act as one source of truth for the table storage access. By enabling Storage Based Authorization in the Metastore Server, you can use this single source for truth and have a consistent data and metadata authorization policy. To control metadata access on the metadata objects such as Databases, Tables and Partitions, it checks if you have permission on corresponding directories on the file system. You can also protect access through HiveServer2 (use case 2b above) by ensuring that the queries run as the end user (hive.server2.enable.doAs option should be "true" in HiveServer2 configuration – this is a default value).
这里面还有个jira bug, 在storage based authorization中, 有些metastore操作并不会触发走hdfs鉴权. 后来推荐使用sql authorization了, 这个bug也就不管了.
https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/HIVE-3009
Operations such as DESCTABLE and DROPDATABASE have null for required privileges.
As part of design, it was decided that metastore-level security for show/describe was difficult to separate form client-side security, which is inherently insecure, and thus, the truly secure model is to use something like HiveServer2, lock down the metastore and not allow any outside access to it, and then use SQL standard authorization on top of that.
hive sql standard based authorization
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+Authorization
sql类的授权, 一个诉求是为了解决字段和hive view的授权问题, 因为hdfs授权只能判断到文件级别, 也就是tables.对接 hive server2, 解决了这个问题.
Although Storage Based Authorization can provide access control at the level of Databases, Tables and Partitions, it can not control authorization at finer levels such as columns and views because the access control provided by the file system is at the level of directory and files. A prerequisite for fine grained access control is a data server that is able to provide just the columns and rows that a user needs (or has) access to. In the case of file system access, the whole file is served to the user. HiveServer2 satisfies this condition, as it has an API that understands rows and columns (through the use of SQL), and is able to serve just the columns and rows that your SQL query asked for.
hive cli命令不提供sql based授权, 是因为hive cli可以直接读取hdfs. hive社区决定直接不支持hive cli, 免得用户以为通过sql可以控制得住.
Note that for use case 2a (Hive command line) SQL Standards Based Authorization is disabled. This is because secure access control is not possible for the Hive command line using an access control policy in Hive, because users have direct access to HDFS and so they can easily bypass the SQL standards based authorization checks or even disable it altogether. Disabling this avoids giving a false sense of security to users.
hive sql授权详细介绍
SQL Standard Based Hive Authorization
默认的hive授权并不是为了防止恶意访问, 只是为了防止错误访问, 也就是其实只是个君子协议.
The default authorization in Hive is not designed with the intent to protect against malicious users accessing data they should not be accessing. It only helps in preventing users from accidentally doing operations they are not supposed to do. It is also incomplete because it does not have authorization checks for many operations including the grant statement. The authorization checks happen during Hive query compilation. But as the user is allowed to execute dfs commands, user-defined functions and shell commands, it is possible to bypass the client security checks.
storage based authorization, 在metastore api调用的时候会触发hdfs鉴权. 不过不支持column/row/view这些精细授权.
Hive also has support for storage based authorization, which is commonly used to add authorization to metastore server API calls (see Storage Based Authorization in the Metastore Server). As of Hive 0.12.0 it can be used on the client side as well. While it can protect the metastore against changes by malicious users, it does not support fine grained access control (column or row level).
sql based authorization授权, 建议是让sql都通过hive server2访问, 然后禁止其他的访问方式.
This authorization mode can be used in conjunction with storage based authorization on the metastore server. Like the current default authorization in Hive, this will also be enforced at query compilation time. To provide security through this option, the client will have to be secured. This can be done by allowing users access only through Hive Server2, and by restricting the user code and non-SQL commands that can be run. The checks will happen against the user who submits the request, but the query will run as the Hive server user. The directories and files for input data would have read access for this Hive server user. For users who don’t have the need to protect against malicious users, this could potentially be supported through the Hive command line as well.
没想到竟然支持sql类型直接授权操作, 支持角色创建 create role / drop role, 支持授权 grant / revoke语句, 平时倒没怎么用过. ranger hive插件也支持这些语句, 将sql语句转化为ranger api请求, 创建role和policy策略.
提供了crud的权限.
- SELECT privilege – gives read access to an object.
- INSERT privilege – gives ability to add data to an object (table).
- UPDATE privilege – gives ability to run update queries on an object (table).
- DELETE privilege – gives ability to delete data in an object (table).
- ALL PRIVILEGES – gives all privileges (gets translated into all the above privileges)
库表等各种操作对应的权限图也提供了, 下面为部分截图
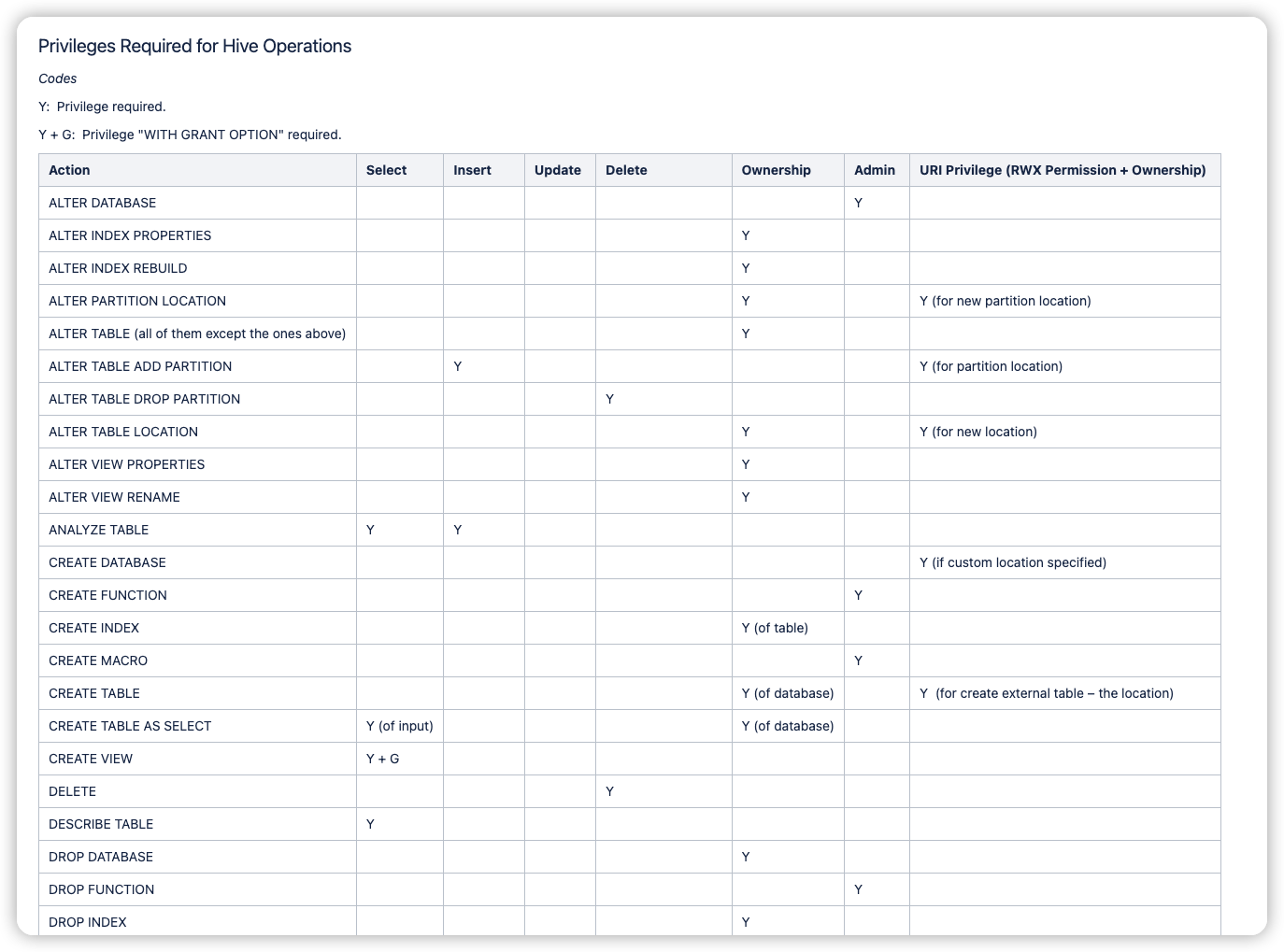
hive 授权sql语句
CREATE ROLE role_name;
Lists all roles and users who belong to this role.
SHOW PRINCIPALS role_name;
GRANT
priv_type [, priv_type ] ...
ON table_or_view_name
TO principal_specification [, principal_specification] ...
[WITH GRANT OPTION];
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000/default> grant select on table secured_table to role my_role;
No rows affected (0.046 seconds)
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000/default> revoke update, select on table secured_table from role my_role;
No rows affected (0.028 seconds)
Find out the privileges all users have on table hivejiratable:
0: jdbc:hive2://localhost:10000> show grant on table hivejiratable;
+-----------+----------------+------------+---------+-----------------+-----------------+------------+---------------+----------------+----------+
| database | table | partition | column | principal_name | principal_type | privilege | grant_option | grant_time | grantor |
+-----------+----------------+------------+---------+-----------------+-----------------+------------+---------------+----------------+----------+
| default | hivejiratable | | | ashutosh | USER | DELETE | false | 1398303419000 | thejas |
| default | hivejiratable | | | ashutosh | USER | SELECT | false | 1398303407000 | thejas |
| default | hivejiratable | | | navis | USER | INSERT | false | 1398303650000 | thejas |
| default | hivejiratable | | | navis | USER | SELECT | false | 1398303650000 | thejas |
| default | hivejiratable | | | public | ROLE | SELECT | false | 1398303481000 | thejas |
| default | hivejiratable | | | thejas | USER | DELETE | true | 1398303380000 | thejas |
| default | hivejiratable | | | thejas | USER | INSERT | true | 1398303380000 | thejas |
| default | hivejiratable | | | thejas | USER | SELECT | true | 1398303380000 | thejas |
| default | hivejiratable | | | thejas | USER | UPDATE | true | 1398303380000 | thejas |
+-----------+----------------+------------+---------+-----------------+-----------------+------------+---------------+----------------+----------+
hdfs 认证鉴权的问题
HDFS Permissions Guide
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/stable/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-hdfs/HdfsPermissionsGuide.html
官方文档很多时候真是把什么都告诉你了, 但是没有去接触到相关领域的时候, 压根看不懂文档里都在讨论什么细碎的问题. 比如这片hdfs权限文档, 如果压根没接触hdfs认证鉴权的问题, 对于开发者而言只是写个程序读写hdfs, 完全没必要理解这里面的弯弯绕绕. 看完也就忘了, 不会去了解这里面的许多细节. 不过接触了hdfs认证鉴权, 并且看了源码和做了一些测试之后,看官方文档感觉就是高度浓缩的红宝书了.
比如这里面讨论hdfs的路径权限问题, 介绍了traverse access的要求, 要进入任何文件目录, 都需要上级所有父级目录的x权限. (不过切换为使用ranger hdfs后, ranger修改了这个原则, 只需要当前目录的x权限即可, 具体可以看ranger的文档和ranger hdfs plugin的代码)
Each HDFS operation demands that the user has specific permissions (some combination of READ, WRITE and EXECUTE), granted through file ownership, group membership or the other permissions. An operation may perform permission checks at multiple components of the path, not only the final component. Additionally, some operations depend on a check of the owner of a path.
All operations require traversal access. Traversal access demands the EXECUTE permission on all existing components of the path, except for the final path component. For example, for any operation accessing /foo/bar/baz, the caller must have EXECUTE permission on /, /foo and /foo/bar.
比如这里详细介绍了hdfds权限系统里的常见概念, 比如ownership路径负责人, parent上级路径, ancestor有效上级路径.
The following table describes the permission checks performed by HDFS for each component of the path.
- Ownership: Whether or not to check if the caller is the owner of the path. Typically, operations that change the ownership or permission metadata demand that the caller is the owner.
- Parent: The parent directory of the requested path. For example, for the path /foo/bar/baz, the parent is /foo/bar.
- Ancestor: The last existing component of the requested path. For example, for the path /foo/bar/baz, the ancestor path is /foo/bar if /foo/bar exists. The ancestor path is /foo if /foo exists but /foo/bar does not exist.
- Final: The final component of the requested path. For example, for the path /foo/bar/baz, the final path component is /foo/bar/baz.
- Sub-tree: For a path that is a directory, the directory itself and all of its child sub-directories, recursively. For example, for the path /foo/bar/baz, which has 2 sub-directories named buz and boo, the sub-tree is /foo/bar/baz, /foo/bar/baz/buz and /foo/bar/baz/boo.
这张图也比较给力, 将hdfs的操作和对应需要的权限解释的非常清楚. 在测试hdfs ranger权限的时候, 就能够知道要授予什么权限了. 比如删除文件, 需要父级目录的write权限; 比如创建文件夹, 需要有效上级目录的write权限. 除了traversal x权限ranger修改了, 其他权限需求基本是相同的.
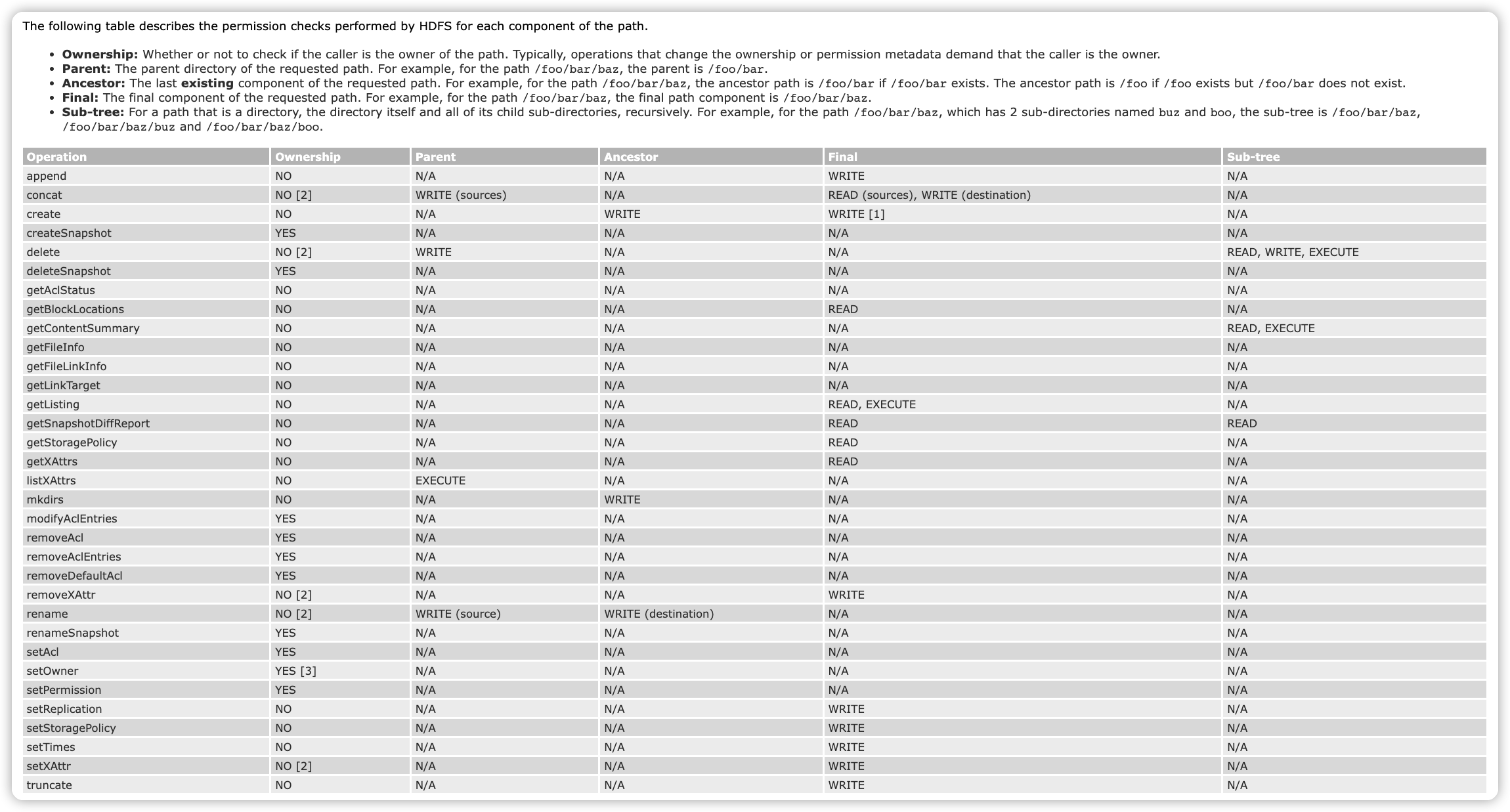
- [1] WRITE access on the final path component during create is only required if the call uses the overwrite option and there is an existing file at the path.
- [2] Any operation that checks WRITE permission on the parent directory also checks ownership if the sticky bit is set.
- [3] Calling setOwner to change the user that owns a file requires HDFS super-user access. HDFS super-user access is not required to change the group, but the caller must be the owner of the file and a member of the specified group.
hdfs的一些权限的基础概念
The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) implements a permissions model for files and directories that shares much of the POSIX model. Each file and directory is associated with an owner and a group. The file or directory has separate permissions for the user that is the owner, for other users that are members of the group, and for all other users. For files, the r permission is required to read the file, and the w permission is required to write or append to the file. For directories, the r permission is required to list the contents of the directory, the w permission is required to create or delete files or directories, and the x permission is required to access a child of the directory.
Each client process that accesses HDFS has a two-part identity composed of the user name, and groups list. Whenever HDFS must do a permissions check for a file or directory foo accessed by a client process,
- If the user name matches the owner of foo, then the owner permissions are tested;
- Else if the group of foo matches any of member of the groups list, then the group permissions are tested;
- Otherwise the other permissions of foo are tested.
一些acl的介绍
一个文件支持配置多个用户和用户组的访问权限
In addition to the traditional POSIX permissions model, HDFS also supports POSIX ACLs (Access Control Lists). ACLs are useful for implementing permission requirements that differ from the natural organizational hierarchy of users and groups. An ACL provides a way to set different permissions for specific named users or named groups, not only the file’s owner and the file’s group.
By default, support for ACLs is enabled, and the NameNode allows creation of ACLs. To disable support for ACLs, set dfs.namenode.acls.enabled to false in the NameNode configuration.
Only directories may have a default ACL. When a new file or sub-directory is created, it automatically copies the default ACL of its parent into its own access ACL. A new sub-directory also copies it to its own default ACL. In this way, the default ACL will be copied down through arbitrarily deep levels of the file system tree as new sub-directories get created.
acl配置样例
user::rwx
group::r-x
other::r-x
default:user::rwx
default:user:bruce:rwx #effective:r-x
default:group::r-x
default:group:sales:rwx #effective:r-x
default:mask::r-x
default:other::r-x
一些acl操作命令
ACLs Shell Commands
hdfs dfs -getfacl [-R] <path>
Displays the Access Control Lists (ACLs) of files and directories. If a directory has a default ACL, then getfacl also displays the default ACL.
hdfs dfs -setfacl [-R] [-b |-k -m |-x <acl_spec> <path>] |[--set <acl_spec> <path>]
Sets Access Control Lists (ACLs) of files and directories.
这个命令如果文件上有"+"号, 说明有acl控制.
hdfs dfs -ls <args>
The output of ls will append a ‘+’ character to the permissions string of any file or directory that has an ACL.
See the File System Shell documentation for full coverage of these commands.
一些配置项
平时几乎没看过 Configuration Parameters
dfs.permissions.enabled = true
If yes use the permissions system as described here. If no, permission checking is turned off, but all other behavior is unchanged. Switching from one parameter value to the other does not change the mode, owner or group of files or directories. Regardless of whether permissions are on or off, chmod, chgrp, chown and setfacl always check permissions. These functions are only useful in the permissions context, and so there is no backwards compatibility issue. Furthermore, this allows administrators to reliably set owners and permissions in advance of turning on regular permissions checking.
dfs.web.ugi = webuser,webgroup
The user name to be used by the web server. Setting this to the name of the super-user allows any web client to see everything. Changing this to an otherwise unused identity allows web clients to see only those things visible using “other” permissions. Additional groups may be added to the comma-separated list.
dfs.permissions.superusergroup = supergroup
The name of the group of super-users.
fs.permissions.umask-mode = 0022
The umask used when creating files and directories. For configuration files, the decimal value 18 may be used.
dfs.namenode.acls.enabled = true
Set to true to enable support for HDFS ACLs (Access Control Lists). By default, ACLs are enabled. When ACLs are disabled, the NameNode rejects all attempts to set an ACL.
hdfs 认证问题
看官方文档总能看到一些之前没注意过的关键细节.
比如对于kerberos的princial, hdfs只会识别最前面的缩写, a principal todd/foobar@CORP.COMPANY.COM will act as the simple username todd on HDFS.
比如simple认证, 哪个用户登录, 用户名等同于whoammi命令的执行结果, 我记得还可以设置hadoop user环境变量,
export HADOOP_USER_NAME= abc
hdfs dfs -put <source> <destination>
As of Hadoop 0.22, Hadoop supports two different modes of operation to determine the user’s identity, specified by the hadoop.security.authentication property:
- simple
In this mode of operation, the identity of a client process is determined by the host operating system. On Unix-like systems, the user name is the equivalent of whoami.
- kerberos
In Kerberized operation, the identity of a client process is determined by its Kerberos credentials. For example, in a Kerberized environment, a user may use the kinit utility to obtain a Kerberos ticket-granting-ticket (TGT) and use klist to determine their current principal. When mapping a Kerberos principal to an HDFS username, all components except for the primary are dropped. For example, a principal todd/foobar@CORP.COMPANY.COM will act as the simple username todd on HDFS.
其他顺带关注的内容
hccatalog的介绍
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/HCatalog+UsingHCat
HCatalog is a table and storage management layer for Hadoop that enables users with different data processing tools — Pig, MapReduce — to more easily read and write data on the grid. HCatalog’s table abstraction presents users with a relational view of data in the Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS) and ensures that users need not worry about where or in what format their data is stored — RCFile format, text files, SequenceFiles, or ORC files.
HCatalog supports reading and writing files in any format for which a SerDe (serializer-deserializer) can be written. By default, HCatalog supports RCFile, CSV, JSON, and SequenceFile, and ORC file formats. To use a custom format, you must provide the InputFormat, OutputFormat, and SerDe.

hive cli 的权限问题
Beeline Authentication with Ranger vs. Hive CLI
Hive CLI bypasses all the security policies.
- beeline与hive server2交互, 受到 sql authorization 的管控
- hive cli 绕过了防护, 只能通过hdfs权限进行管控
How to disable hive shell for all users (Hive CLI)
社区里的建议, 都是悄悄屏蔽hive cli命令, 但都只是君子协议.
We can add below lines in hive-env template via ambari to disable hive-shell
if [ "$SERVICE" = "cli" ]; then
echo "Sorry! I have disabled hive-shell"
exit 1
fi
After restarting hive services, when you try to run hive shell then you will get below output
[root@sandbox hive]# hive
Sorry! I have disabled hive-shell
其他参考文档
ibm hive sql介绍
之前看过几篇ibm的大数据介绍文档, 都挺全面的, 大公司认真写文档还是值得称赞.
hive-storage-based-authorization
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/db2-big-sql/5.0.1?topic=hive-storage-based-authorization
When the metastore server security is configured to use Storage-Based Authorization, it uses the file system permissions for folders corresponding to the different metadata objects as the source of verification for the authorization policy. Using this authorization method is recommended in the metastore server.
In Hive, there is a corresponding directory to a database or table for each file system that is used for storage. Using this authorization model, the read/write permissions for this directory also determines the permissions a user, or group, will have to the database or table.

SQL-Standard Based Authorization
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/db2-big-sql/5.0.1?topic=hive-sql-standard-based-authorization
Use SQL-Standard Based Authorization to enable fine grained access control. It is based on the SQL standard for authorization, and uses the familiar GRANT/REVOKE statements to control access. You enable it through HiveServer2 configuration.
Privileges are granted to users and/or roles, where any user can be assigned to one or more roles. The public and admin roles have special meaning: The public role includes all users. This role can be used in a GRANT statement to assign a privilege to every user.
The admin role is required to run certain commands, such as the ADD JAR command, and it also allows access to certain objects even where access may not have been explicitly granted to the user.
hive与hidfs结合需要考虑的问题
Ranger: Things to consider for a Hive + HDFS Usecase
https://www.ibm.com/support/pages/ranger-things-consider-hive-hdfs-usecase
这篇ibm的文章也不错, 讨论了下hdfs与hive在权限管理上需要协同处理的问题. 不过不知道是哪一年的文章了, 看讨论的内容, 估计也是好多年前了..
提供的思路是可以不用启用所有的ranger插件, 参考不同场景, 只启用hdfs ranger, 或者只启用hive ranger, 当然总归是有场景不符合的.
hive Non-Impersonation访问, 关闭hive.server2.enable, 那么只需要关注hive sql授权, hdfs的访问都由hive主账号代理, 只需要给这个主账号权限就行了, 非常方便.
hive Impersonation 访问, 开启hive.server2.enable, 那么每个hive sql对底层hdfs的操作都是用当前用户执行, 因此需要考虑用户在hdfs上的权限问题. 建议是直接关闭hive sql访问, 只交给hdfs拦截. 不过这里面也会不少问题, 比如字段权限, view权限等.
Non-Impersonation Usecase For better security control, it is desirable to clamp down the access at the lower levels and control access at higher service levels. In case of a Hive + HDFS usecase, this would mean disabling Impersonation via the hive.server2.enable.doAs property and enabling SQL Standard Authorization in Hive. End users connecting to Hive are then vetted by Hive and allowed read/write access to data only if that permission is granted for the user in Hive. The actual data residing in HDFS is only accessible to service users like hive.
Impersonation Usecase If there are multiple services that need access to the data residing in HDFS, then HDFS becomes the central place to put all the security controls and have other services impersonate the end users while accessing the data. This provides for consistent security controls across the multiple services to access the same data. Read/write permissions to the data are given by way of rwx permissions or ACLs in HDFS.
hive 授权的建议
Best Practices for Hive Authorization Using Apache Ranger in HDP 2.2
https://blog.cloudera.com/best-practices-for-hive-authorization-using-apache-ranger-in-hdp-2-2/
这个是2015年的文章了, 算是非常古老了, 只能大概看看操作截图.
主要也是讨论了hive和hdfs的授权配合问题.
- 只使用hiveserver2, 不使用hdfs的话, 可以配置
hive.server2.enable.doAs为false, 使用hive主账号去访问hdfs. - 同时使用hiveserver2和hdfs, 在ranger权限上同时配置hive策略和hdfs策略.
也讨论了hive cli的问题, hive cli直接读写hdfs里的文件, 因此hive ranger plugin是管控不到的.
Hive CLI loads hive configuration into the client and gets data directly from HDFS or through map reduce/Tez tasks. The best way to protect Hive CLI would be to enable permissions for HDFS files/folders mapped to the Hive database and tables. In order to secure metastore, it is also recommended to turn on storage-based authorization.
Please note that Ranger Hive plugin only applies to Hiveserver2. Hive CLI should be protected using permissions at the HDFS folder/file level using Ranger or HDFS ACLs.
hdfs 授权的建议
Best practices in HDFS authorization with Apache Ranger
https://blog.cloudera.com/best-practices-in-hdfs-authorization-with-apache-ranger/
2016年的文章, 主要是建议/user目录和/tmp目录由hadoop原生进行管控, 而不是通过ranger进行管控.
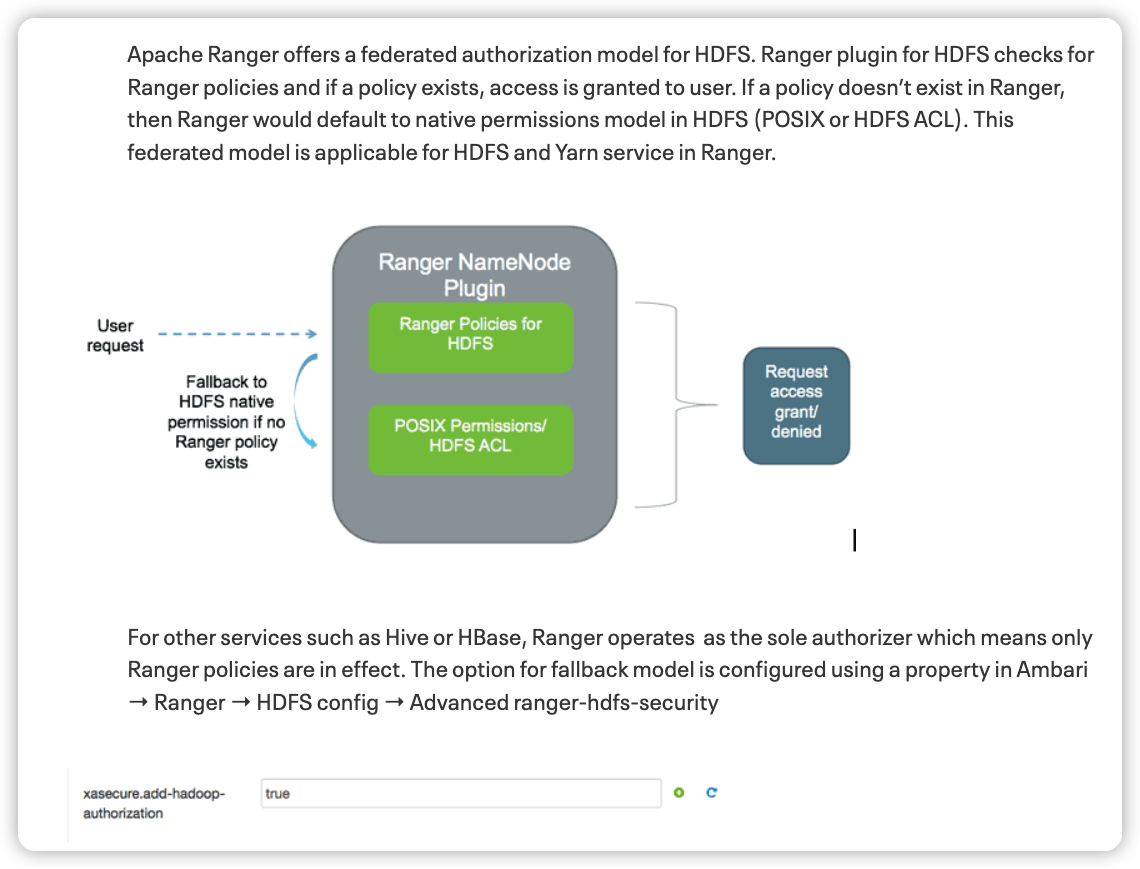
hdfs策略模型在没有一条ranger policy被权限请求匹配到的时候, 会切换到hdfs原生进行鉴权. 这种策略在存量大数据集群升级切换到ranger上很有用, 属于无缝切换.
不过这也是需要配置的, 如果配置 xaseucre.add-hadoop-authorization为false, 则只会走ranger鉴权, 没有配置的访问都会被默认拒绝. 经过测试, 目前腾讯云emr3.5版本开启ranger后, 默认是关闭fallback到acl的. 在ranger审计日志里也能够发现这个信息, 一般的ranger鉴权通过/拒绝都在ranger审计里留下记录, 表明这是被ranger-acl鉴权, 并且展示了关联的policy 策略; 如果走的是ranger无策略匹配拒绝的路线, 关联的policy字段为空; 如果是被acl拒绝, ranger审计里(可能)没有留下信息, or hadoop-acl.
看ranger审计日志, 是快速入门ranger代码和熟悉ranger策略行为的绝佳方法.
The federated authorization model enables customers to safely implement Ranger in an existing cluster without affecting jobs which rely on POSIX permissions. We recommend to enable this option as the default model for all deployments.
After Apache Ranger and Hadoop have been installed, we recommend administrators to implement the following steps:
- Change HDFS umask to 077
- Identify directory which can be managed by Ranger policies
- Identify directories which need to be managed by HDFS native permissions
- Enable Ranger policy to audit all records
特殊目录的建议详情
/user和/tmp目录建议使用hadoop原生体系, 设置/user子目录为700, 只给创建者使用. 这两个目录主要是被应用创建和使用, 估计创建者就是用户身份. 测试发现确实如此, hive mr的时候/user目录创建被ranger拦截住, 审计信息里的操作用户就是当前用户. 至于父级目录user本身, 估计应该要给非递归的rwx权限, 不然就无法创建子目录, 并且进入子目录了. 上级目录/user给rwx权限其实也有风险, 虽然用户可以创建自己的文件夹, 并且无法进入其他用户的文件夹, 但是可以直接删除其他用户的文件夹, 毕竟w权限没有区分create还是delete. 有一个绕行方案, /user只给root用户, 子目录也由root创建, 不过接下来chown修改拥有者为子用户, 并且设置700.
很多时候, hdfs ranger策略里都有*路径的策略用于放开某些超级用户. 这条全局策略会导致所有的hdfs请求都会至少匹配到一条策略, 导致无法切换到hdfs原生权限. 因此看到的不少业务系统, 其实都交给ranger进行管控了, 并没有使用posix/acl体系.
Identify directories which can be managed by HDFS permissions
It is recommended to let HDFS manage the permissions for /tmp and /user folders. These are used by applications and jobs which create user level directories.
Here, you should also set the initial permission for `/user`` folder to “700”, similar to the example below
hdfs dfs -ls /user
Found 4 items
drwxrwx— – ambari-qa hdfs 0 2015-11-30 07:56 /user/ambari-qa
drwxr-xr-x – hcat hdfs 0 2015-11-30 08:01 /user/hcat
drwxr-xr-x – hive hdfs 0 2015-11-30 08:01 /user/hive
drwxrwxr-x – oozie hdfs 0 2015-11-30 08:02 /user/oozie
$ hdfs dfs -chmod -R 700 /user/*
$ hdfs dfs -ls /user
Found 4 items
drwx—— – ambari-qa hdfs 0 2015-11-30 07:56 /user/ambari-qa
drwx—— – hcat hdfs 0 2015-11-30 08:01 /user/hcat
drwx—— – hive hdfs 0 2015-11-30 08:01 /user/hive
drwx—— – oozie hdfs 0 2015-11-30 08:02 /user/oozie
网易数帆的技术分享
update: 看到了网易数帆在2023年的分享文章, 非常赞. 很多细节都是真实面临的问题, 这个领域需要面对解决的问题, 许多人早就解决过了. 看起来网易是扎扎实实一步一步在做数据治理的产品, 想起来apache kyuubi也是网易出品的, 那些到处瞎搞纯捞钱的公司可没有精力搞这种开源组件.
网易基于Apache Ranger的数据安全中心实践
https://www.secrss.com/articles/55600
快速摘录的知识点:
- 部分自定义的ranger插件, 将plugin的policy鉴权修改为web调用, 而不是本地缓存, 看起来与前面腾讯的方案相同. 解决了十百万级策略数量下policy占用组件内存的问题, 但引入的问题是如果组件与安全平台部署过远, 鉴权速度会有问题.
- 大家都会遇到所谓管理平台与ranger策略一致性的问题, 网易解决思路是只写入ranger, 读取的话则从ranger定时同步到安全平台自己的缓存中. 虽然有时间差, 但是高一致性.
- 大家都会遇到的ranger不支持搜索某个用户有哪些权限, ranger admin本身bug多 api速度慢的问题, 网易的思路是自己构建权限模型, 从ranger缓存策略到自己的权限模型上. 一些读取和筛选的操作, 就都在自己的权限模型上进行操作, 这样自由度就非常高了. ranger作为最终一致性的管控中心, 只负责权限的写入.
- 大家都会遇到某些高级企业用户就是想要自己管控ranger策略的问题, 不想由定制化的平台去接管. 这样就触发了一个需求, 在ranger里的管控需要体现在自己的安全平台上, 同时安全平台不能自己去实现一些隐含的自定义权限. 网易开放了ranger的接口, 另外前面的policy一致性管理策略也刚好解决了这个问题, 写入都到ranger中, 安全平台只会定时从ranger读取policy作为缓存. 不过这里还是有个问题,安全平台如果还要支持授权回收/角色管理权限等业务需求, 如何保持与ranger里的一致呢, 难道安全平台本身只能做policy的缓存中介?
- hdfs权限的w包含了delete, 网易改写了权限请求, 并且设置了安全目录禁止删除
- 动态脱敏部分的解决方案也不错, 在ranger里记录的只是一个脱敏策略的标识, 具体的脱敏算法由平台提供. 同时提供白名单用户机制, 某张表白名单里的用户就不用走脱敏了. 高级用户的需求挺广泛的.
- 大家都会遇到权限策略管理问题, 比如无效权限, 冗余权限. 网易是做了权限的管理平台, 并且在审计环节记录权限的使用情况, 可以分析出长时间没用的无效权限. 看起来网易也使用了用户角色去管理权限, 审计平台补全了权限是通过用户还是角色的命中拦截信息.
- hdfs和hive的负责人ownership权限管理问题, 看起来网易也摸索过了. 比如hdfs的递归owner问题, hive metastore的owner字段会被低版本spark污染问题, 网易自己在元数据平台维护了用户负责人, 鉴权的时候需要从元数据平台补全负责人信息. 这里看来实现了元数据采集管理平台与安全鉴权平台的联动. 看起来网易之前也是一张表一条policy记录,有了owner负责人字段后, policy数量可以大量减少, 毕竟可以用库表模糊匹配一条策略授权owner就可以了.
- spark的ranger鉴权和脱敏问题, 看起来是从logical plan执行计划里解析出对应的字段, 再调用原来的逻辑进行处理. 看起来非常熟悉, 最近在kyuubi里看到的鉴权和脱敏插件就是这个思路, 这时候想起来kyuubi就是网易数帆出品的开源组件.
- ranger 里到处都是小bug, 看过ranger源码就有这种感觉了, 尤其是混乱的admin部分.
- 商业化部分也是很有感触, 安全平台需要对接内部产品和外部客户, 这时候就出现了一个问题, 公司内部可以去改造大数据组件进行部署, 但是外部可能只能提供对接开源大数据组件. 对于平台型的大数据产品而言, 很多时候就是这么纠结, 很多方案不能用, 只能把大数据组件开源提供的方案上进行构建.
- 不过看完后还有不少问题, 有没有实现字段级别的鉴权, hive/hdfs这些权限搭配是怎么设计的? 这个坑里到处都是细节的问题.