ranger 标签策略
分类分级系统, 跟标签策略系统真是绝配.
操作ranger界面发现有个tag based policy的页面, 但是不知道怎么联动才能生效; 对应的resource based policy则非常直观, 直接定义某个库表有什么权限. 搜索了一圈, 发现原来ranger已经进化到这种程度了.
所谓的tag就是库表元数据上的标签, 根据标签授予不同的访问策略.之所以没法在ranger上直接体验到 tag based policy的用法, 是因为这个tag并不是在ranger内部操作的, 需要结合外部元数据系统才能使得策略生效, 官方使用的是atlas数据治理系统. atlas提供了数据敏感层级标签, 提供了数据血缘. 内部的业务元数据系统, 估计可以参考改造下.
tag based policy的实现原理也比较简单, 在鉴权的时候, 大数据组件会提供需要鉴权的库表库表和用户信息, 这时候可以查找库表对应的标签, 然后查找对应的策略进行常规鉴权. 资源策略在plugin端使用了json缓存, 元数据的标签信息也可以使用json缓存, 在鉴权的时候都可以在plugin插件内部完成鉴权. 不过如果元数据系统过于庞大, 估计还是得修改为远程调用.
tag based policy 在很多场景都很有用, 业务系统可以很方便构建复杂的业务逻辑. 最常见的是分类分级, 根据不同元数据的敏感级别, 限制不同级别用户的访问. 如果没有标签策略系统, 只依赖于资源策略系统, 每次修改元数据分类分级信息, 都需要操作变更一堆关联策略, crud的批量一致性操作想想就很复杂. 有了标签策略系统, 权限体系压根就无需感知到元数据的变化, 什么都不用做. 因为与具体的元数据信息无关, 同一套标签策略系统还能跨不同集群使用. 有点可以类比ranger的用户组/角色的授权, 以前用户变更某个业务角色需要修改一堆这个角色关联的策略, 有了ranger用户组/角色后, 只需要变更用户的映射信息即可.
很多问题, 换个方案来考虑, 突然就变得非常简单了.
tag base policy 除了可以使用元数据的tag, 也可以使用调用方的tag信息, 比如发起请求的调用者的ip属性, 所在组织信息, 某些特殊参数属性. 这其实属于 ABAC(attribute based access control)的范畴了, 对应的是RBAC(role based access control). 问题又来了, 用户的tag属性信息来自哪里呢? 这块没有仔细去看了, ranger里有个user encrich模块, 估计可以提供一些额外的用户信息, 也支持缓存到plugin插件的机器上.
参考文档
官方cwiki: Tag based policy requirements
Tag based policy requirements
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/RANGER/Tag+based+policy+requirements
标签本身只是普通的标记而已, 可以随便打标签, 也可以根据安全敏感登记
Tag: Tags are arbitrary named strings. Tags are applied on resources, which could be at any granularity that can be identified. E.g. Table Customer can be tagged as PII. Where Customer is the resource and PII is the tag. Tagging of resources enables multiple use cases, e.g. Access Control (who has or doesn’t have access to a resource based on tag), Reporting (who accessed the resources for a given Tag), etc.
标签tag有主标签信息, 比如标签ABCD, 同时也有额外的标签属性信息, 比如90天后失效这种属性, 这也支持在策略里进行配置.
Tag Attribute: When resources are tagged, it can be associated with key/value pairs. E.g. If an customer tax file is stored, then it might be tagged with optional attribute like “ExpiryTime=2022-03-06 GMT”, which means, this document should not be accessible after the ExpiryTime. Similar to Tag, tag attributes are also subject to interpretation by the policy.
标签的外部系统, 推荐使用atlas打标签
Tag Source System: The source of the tag is generally an external system e.g. Apache Atlas. It is highly recommended that there should be only one source of truth for the tags.
ranger 需要定期与标签系统同步
Ranger would need to sync with external metastore to retrieve the classification labels/tag and the associated metadata
Tag Synchronizer: These are custom adaptor process code which is responsible to keep the tagged resources in sync with Ranger. It could be implemented using poll on regular interval or if the source system supports message queue, then this process can subscribe and call the Ranger Tag API to update the Ranger Tag Database.
一个元数据可以被打多个标签, 也支持多个标签配置不同的策略.
If data is classified with multiple tags, there could be a possibility that different policies exists for different tags. Users should be given access if any of the the policies provide access to the user or the group. Exceptions would be sensitive or classified policies where users could be explicitly granted or denied permissions. If a user is denied permission in a policy, it would take precedence over any access given in other policies
官方cwiki: Tag Based Policies
Tag Based Policies
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/RANGER/Tag+Based+Policies
tag-based policy的主要优点是把资源的分类分级管理与授权管理隔离开, 而不是不停的耦合到一起, 简化了业务系统的管理.
One of the important advantage is the separation of resource-classification from access-authorization. For example, resources (HDFS file/directory, Hive database/table/column etc.) containing sensitive data like social-security-number/credit-card-number/sensitive-health-care-data can be tagged with PII/PCI/PHI – either as the resource enters the Hadoop ecosystem or any time later. Once a resource is tagged, the authorization for the tag would automatically be enforced, thus eliminating the need to create or update of policies for the resource. Also, a single authorization policy for a tag can be used to authorize access to resources across various Hadoop components – which eliminates the need to create separate policies in each component.
tag store 缓存tag标签元数据信息
To minimize the performance impact during policy evaluation (in finding tags for resources), Apache Ranger plugins cache the tags and periodically poll the tag store for any changes. On detecting change, the plugins update the cache.
tag sync用于定期同步标签信息. 具体的实现是接受altas的元数据变更通知然后进行同步, 估计也有全量同步.
Tag sync is a daemon process similar to ranger-usersync process.In the current release, ranger-tagsync supports receiving tag details from Apache Atlas via change notifications. As tags are added/updated/deleted to resources in Apache Atlas, ranger-tagsync would receive notifications and update the tag store.
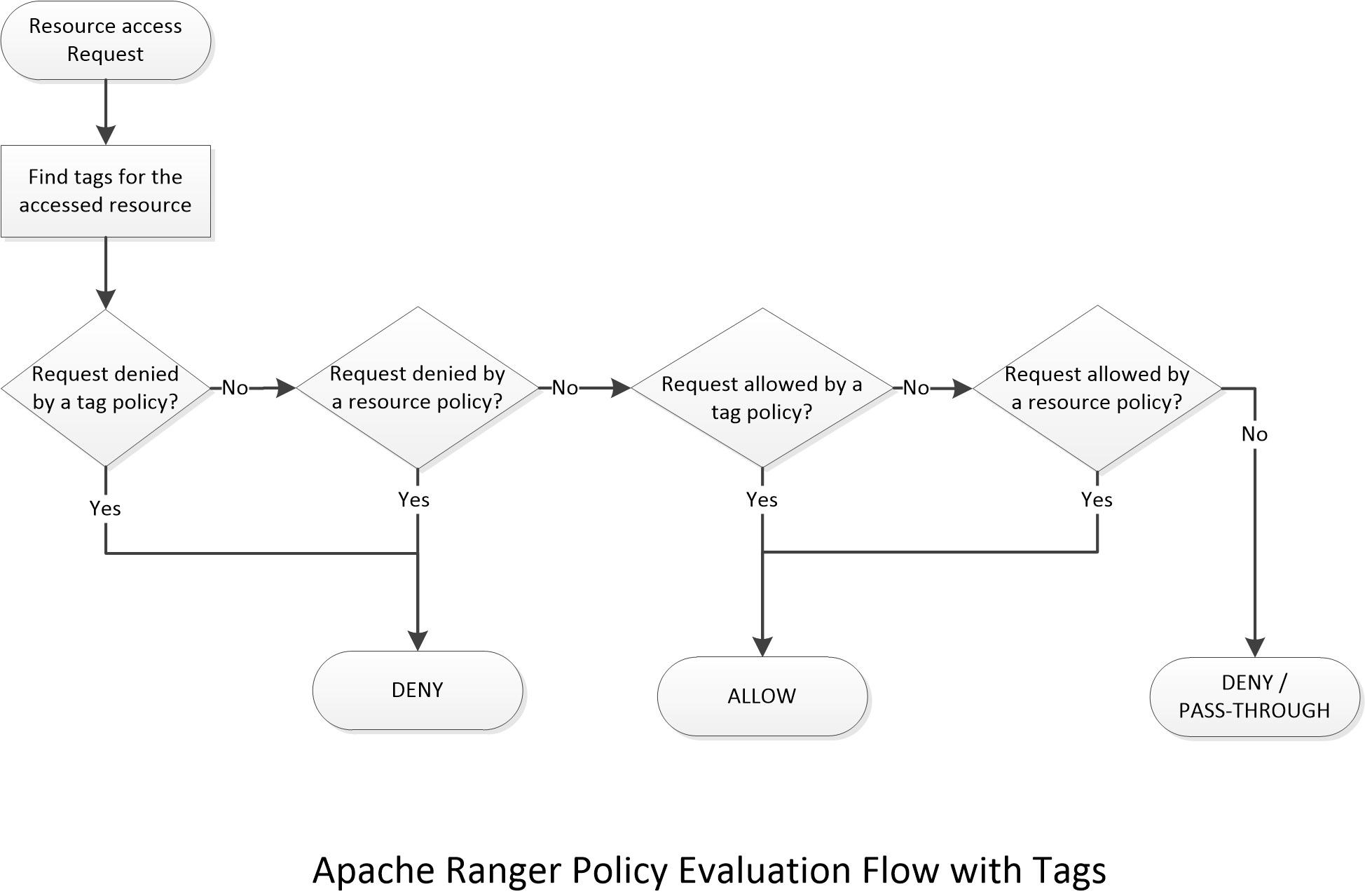
tag标签策略的配置, 最上面的tag name就是匹配的元数据主tag信息, 下面的policy conditions可以设置筛选tag attributed信息, component permissions则定义里能够访问的组件类型. policy conditions里的筛选语法, 用的是js语法.
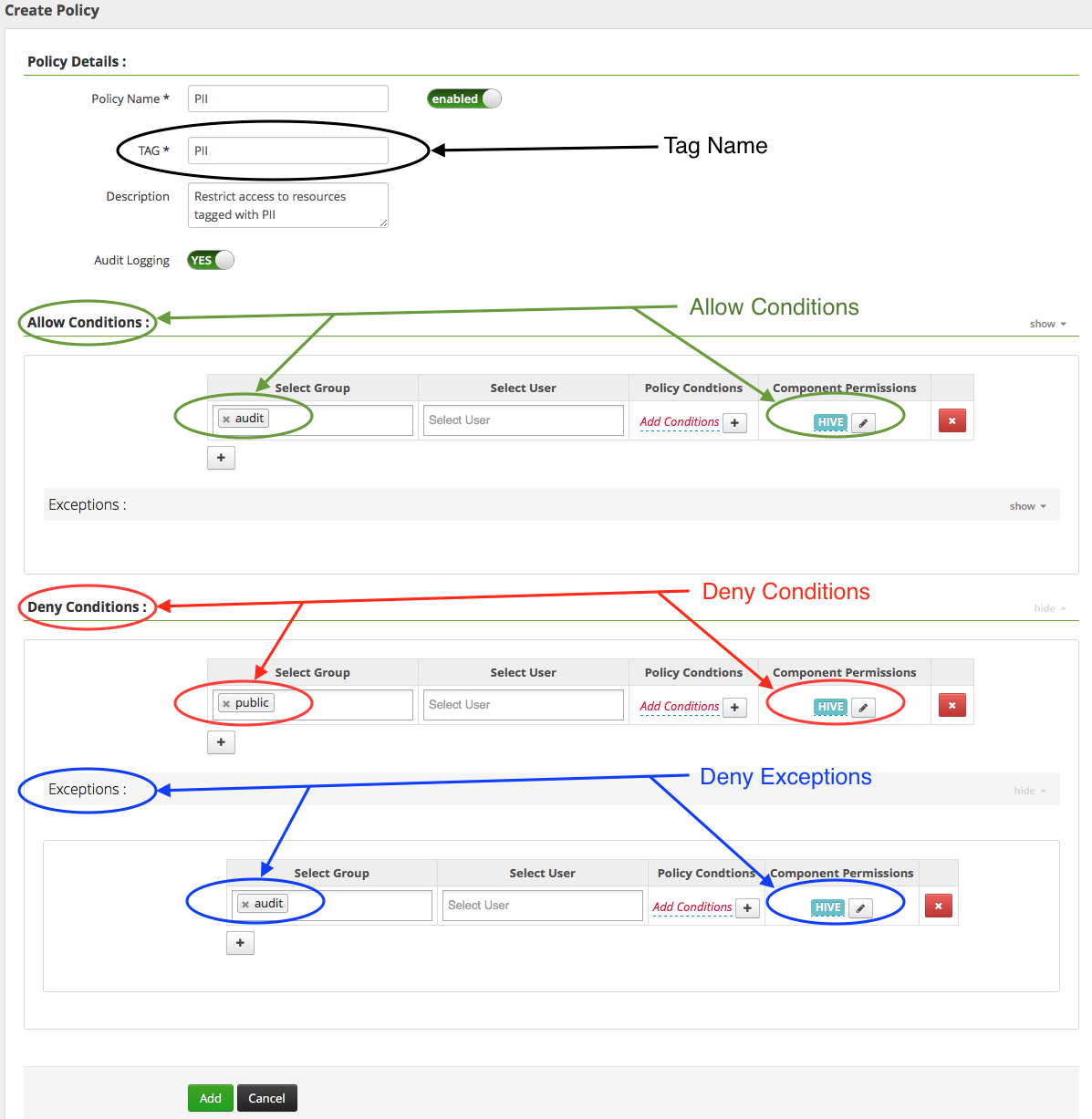
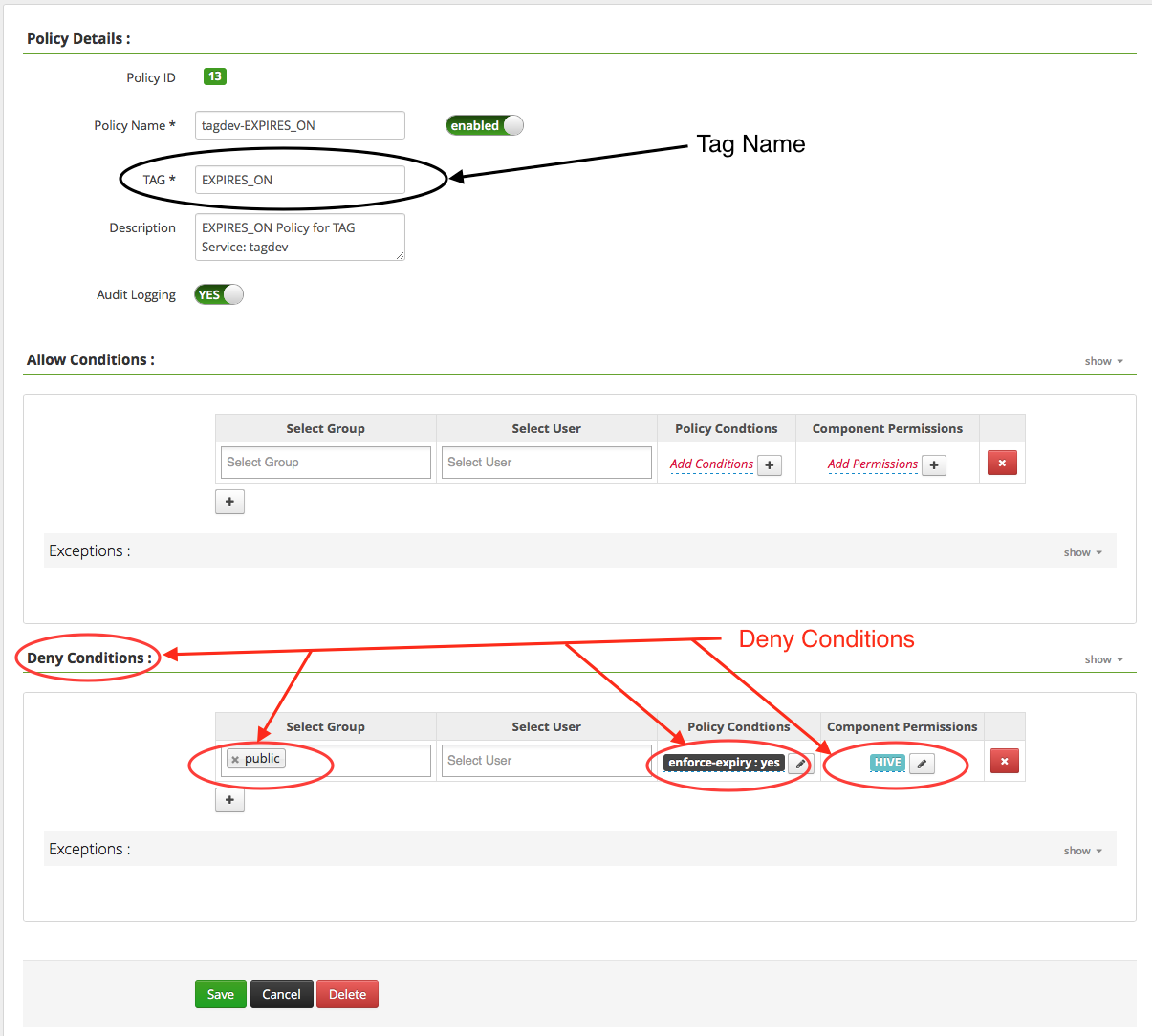
官方博客 Adventures in attribute-based access control (ABAC) - Part 1
Adventures in attribute-based access control (ABAC) - Part 1
https://ranger.apache.org/blogs/adventures_in_abac_1.html
2023年的ranger博客, 提供了一些复杂的策略组合例子, 可以参考, 不过这只是part 1.
高屋建瓴定义总结了ranger里数据访问和用户的几种定义
- 4种数据访问控制: 资源策略, tag策略, 行策略, 脱敏策略 (没想到后两种也算是标准的数据管控)
- 2种用户定义: 用户id或者组内的id; 角色定义. (没想到组id也是属于第一种)
Data can be specified in access control policies in multiple ways:
- Resource-based access control: data is specified by its logical identifier e.g., table name, column name, Kafka topic name, AWS S3 bucket name.
- Tag-based access control (TBAC): data is specified by one or more of its properties, represented by a tag on its metadata, e.g., a Sales Region or Sensitivity Level.
- Row access control: specifies rows/records that are visible to the user at run time by setting up filters based on the value of an attribute, e.g., Sales Region is "US”.
- Masking access control: specifies if the data should be masked before making it available the user.
Users can be specified in access control policies in multiple ways:
- by their individual IDs, or by their group IDs.
- by the roles the users belong to e.g., "USSalesPerson”. This approach is generally called Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
推荐的就是rbac/tbac的访问控制
It’s generally acknowledged that RBAC and TBAC are more maintainable, easier to understand, and therefore less error-prone than resource-based access control and identifying users by their IDs or group IDs. However, these are not sufficient for even moderately complex access control constraints, as we will see.
复杂的场景case案例, 虽然只是用来展示当前组合的限制性, 但也可以拿来看能做到哪种程度
Beyond Tag-based and Role-based Access Control: GlobalSalesPartners
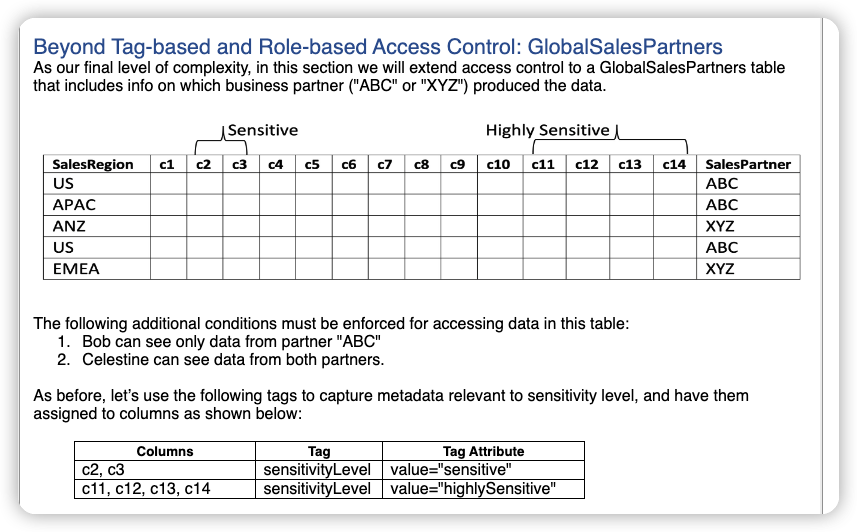
use the following roles to capture the users’ access scope by sensitivity level, region, and sales partner, and assign our users as members of the appropriate roles:
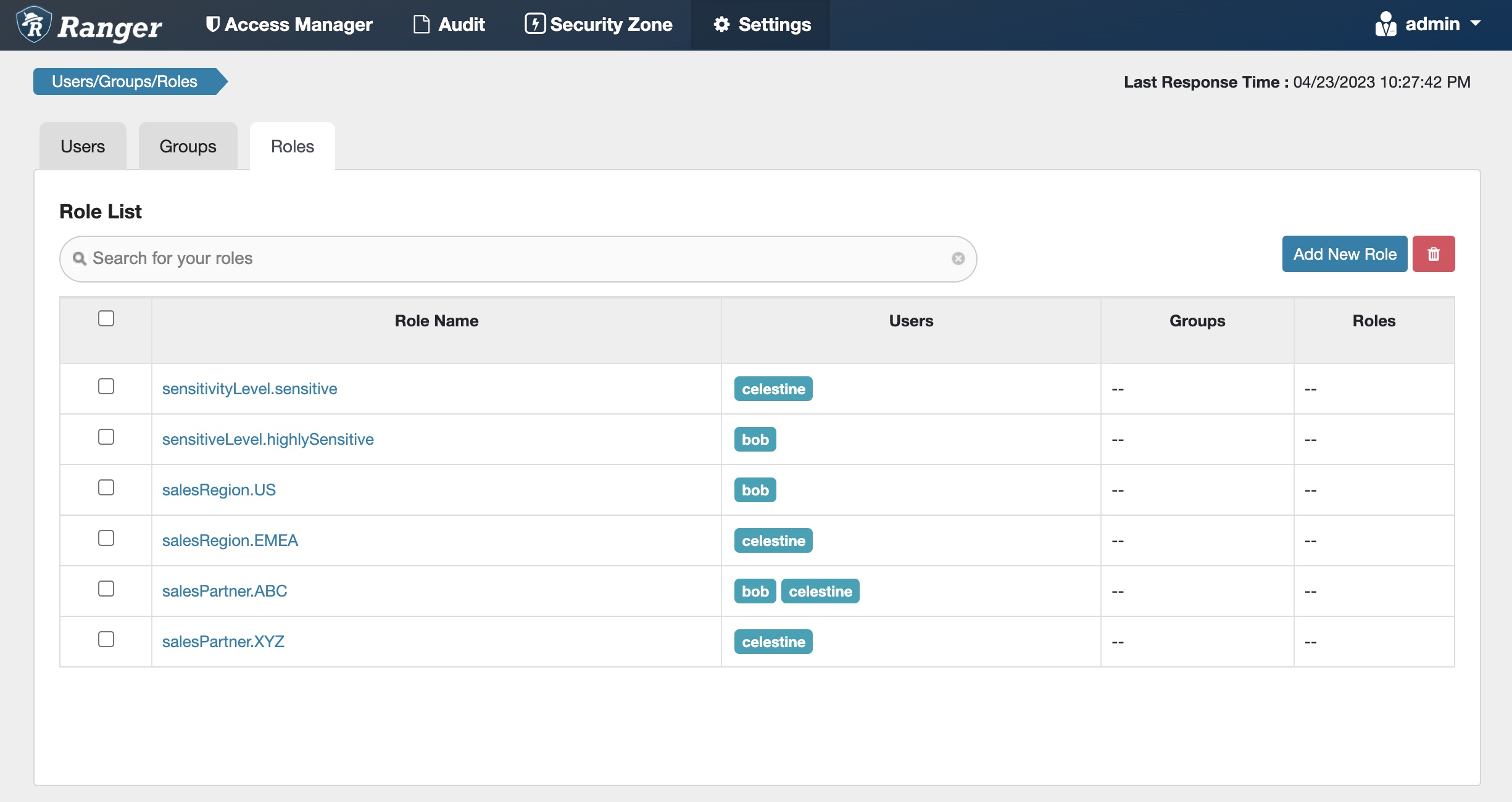
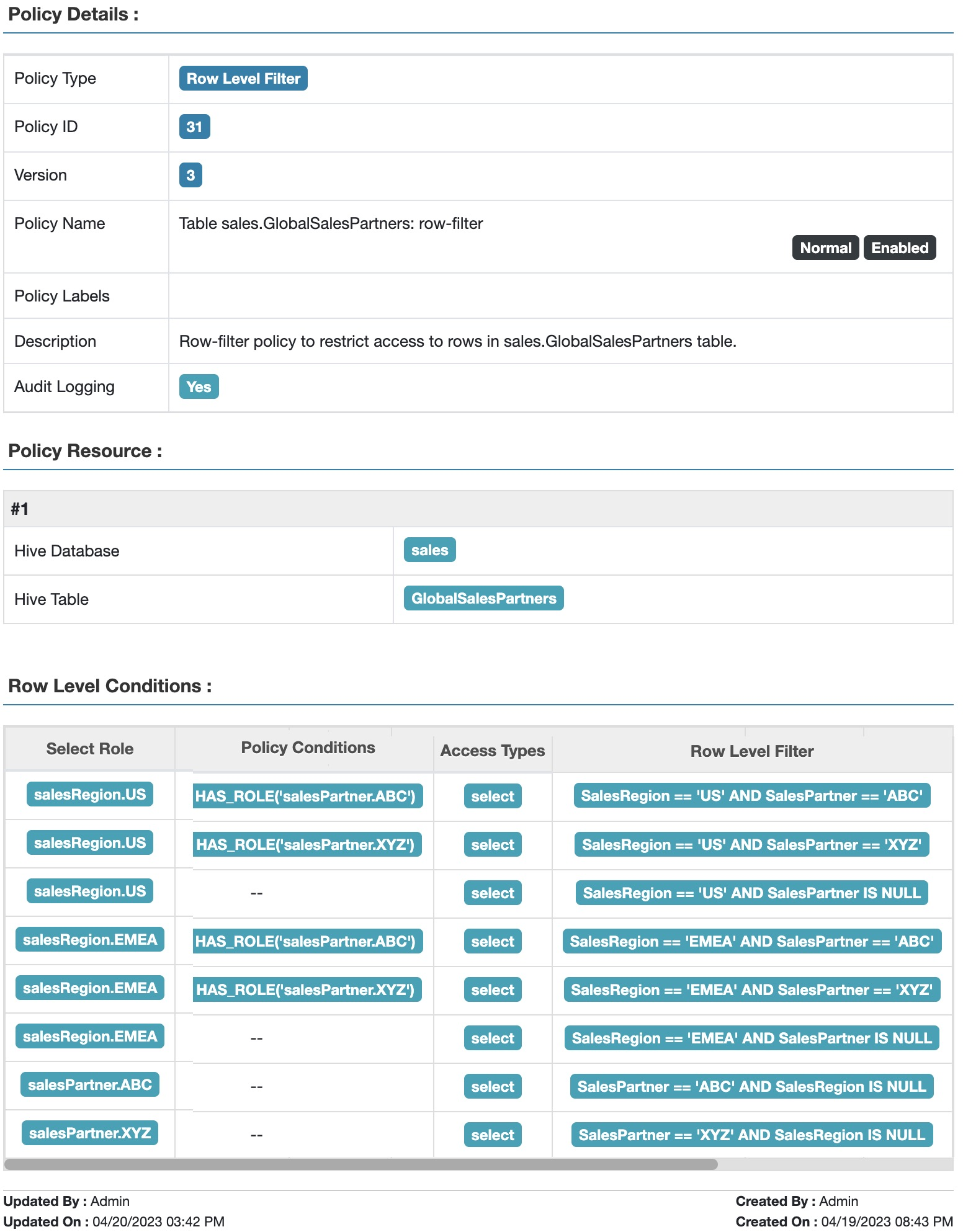
cloudera tag policy 使用指南
Using Tag Attributes and Values in Ranger Tag-Based Policy Conditions
一些tag based policy的使用指南, 包括js语法解析, 元数据信息context和tag属性tagAttr的使用, 用户信息的获取.
得多看看怎么使用的, 不然只看设计文档也不知道怎么用起来.
The policy condition is introduced in the tag service definition:
{
"itemId":2,
"name":"expression",
"evaluator": "org.apache.ranger.plugin.conditionevaluator.RangerScriptConditionEvaluator",
"evaluatorOptions" : {"engineName":"JavaScript", "ui.isMultiline":"true"},
"label":"Enter boolean expression",
"description": "Boolean expression"
}
The following variables can be referenced in the boolean expression:
- ctx: Context handler containing APIs to access metadata information from the request.
- tag: Information about the current tag.
- tagAttr: Map containing all the current tag attributes and corresponding values.
The following APIs available from the request:
- getUser(): Returns a string.
- getUserGroups(): Returns a set of strings containing groups.
- getClientIPAddress(): Returns a string containing client IP address.
- getAction(): Returns a string containing information about the action being requested.
用例case, policy condition的写法
if ( tagAttr.get('ipAddr').equals(ctx.getClientIPAddress()) ) {
ctx.result = true;
}
if (tagAttr.get('ipAddr').equals(ctx.getClientIPAddress()) && ctx.getUser().equals("bob")) {
ctx.result=true;
}
